India’s economic growth over the past few decades has been remarkable, transforming the country into one of the world’s largest economies. However, this growth has been accompanied by increasing income inequality, with the rich benefiting disproportionately more than the poor. This widening gap between the rich and the poor poses a significant challenge to India’s social stability, inclusive development, and long-term economic sustainability.
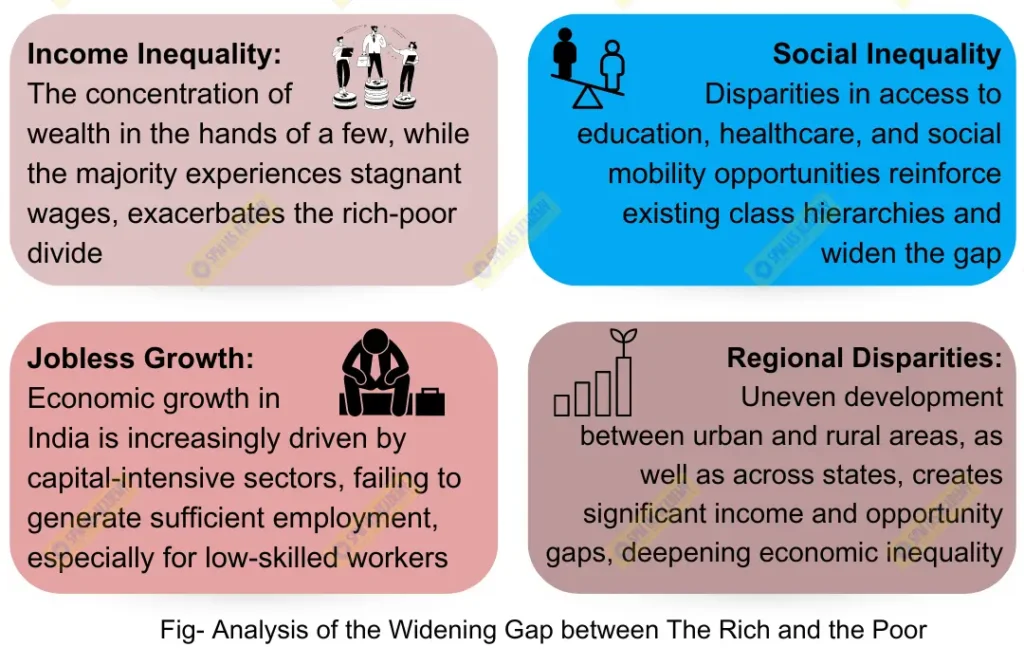
Analysis of the Widening Gap Between the Rich and the Poor
A. Income Inequality
- Skewed Wealth Distribution: A small percentage of the population controls a significant portion of the country’s wealth. According to reports by organizations like Oxfam(“India Inequality Report 2023: The Rise of the Richest 1%“), the richest 1% of Indians hold more than 40% of the national wealth, while the bottom 50% own just a fraction. This disparity has been exacerbated by policies that favor capital over labor and by uneven access to opportunities.
- Urban-Rural Divide: Economic growth has been largely concentrated in urban areas, leading to a significant urban-rural divide. While cities like Mumbai, Delhi, and Bangalore have seen a boom in economic activity, many rural areas still struggle with poverty, lack of infrastructure, and limited access to basic services.
B. Social Inequality
- Caste and Gender Disparities: The benefits of economic growth have not been equally distributed across different social groups. Historically marginalized communities, such as Dalits, Adivasis, and women, continue to face barriers to education, employment, and income opportunities. This social inequality reinforces economic disparities, creating a cycle of poverty and exclusion.
- Educational Inequality: Access to quality education remains unequal, with the wealthy able to afford private schooling and higher education, while the poor often rely on underfunded public schools. This educational gap limits the ability of poorer sections of society to benefit from economic opportunities.
C. Jobless Growth
- Limited Employment Opportunities: Despite economic growth, job creation has not kept pace, particularly in sectors that employ a large number of low-skilled workers, as per the “India Development Report” by the World Bank. The rise of automation and the emphasis on capital-intensive industries have led to jobless growth, where the economy expands without a corresponding increase in employment opportunities.
- Informal Sector Vulnerability: A large portion of India’s workforce is employed in the informal sector, which is characterized by low wages, job insecurity, and a lack of social protection. These workers have not significantly benefited from economic growth, leading to persistent poverty and inequality.
D. Regional Disparities
- Uneven Development: Economic growth has been uneven across different regions, with states like Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu growing faster than states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Odisha. This regional disparity contributes to the overall inequality in the country, as people in less developed regions have fewer opportunities for economic advancement.
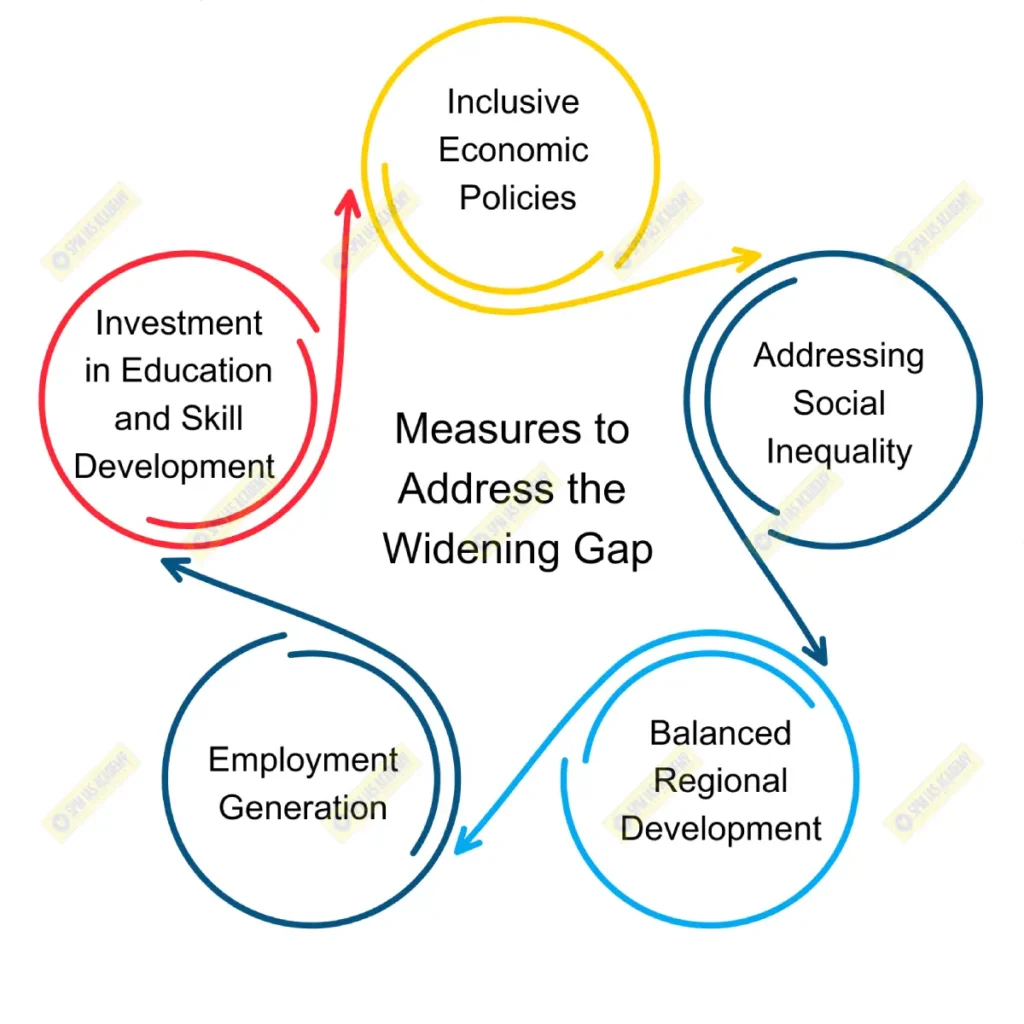
Measures to Address the Widening Gap
A. Inclusive Economic Policies
- Progressive Taxation: Implement a more progressive tax system where the wealthy contribute a fairer share of taxes, which can then be redistributed to support social welfare programs, infrastructure development, and poverty alleviation initiatives.
- Redistributive Policies: Strengthen social safety nets, such as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), public distribution systems, and universal basic income (UBI) schemes to ensure that the poorest sections of society have a minimum level of income security.
B. Investment in Education and Skill Development
- Universal Access to Quality Education: Ensure that all children, regardless of their socio-economic background, have access to quality education. This can be achieved by improving public schooling, investing in teacher training, and providing scholarships for higher education.
- Skill Development Programs: Expand skill development initiatives, like the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), to equip workers, especially those in rural areas and the informal sector, with the skills needed for better-paying jobs in emerging sectors.
C. Employment Generation
- Focus on Labor-Intensive Industries: Promote labor-intensive industries such as textiles, agriculture, and small-scale manufacturing, which have the potential to create a large number of jobs. Support for micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) through easier access to credit and technology can also drive job creation.
- Rural Development Programs: Strengthen rural development initiatives like the National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM) to create sustainable livelihoods in rural areas, reducing the need for migration and ensuring that economic growth reaches the grassroots level.
D. Addressing Social Inequality
- Affirmative Action and Social Inclusion: Strengthen affirmative action policies to ensure that marginalized communities, including Dalits, Adivasis, and women, have equal access to education, employment, and entrepreneurial opportunities.
- Gender Equality Measures: Promote gender equality through policies that support women’s education, participation in the workforce, and access to financial resources. Initiatives like the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao scheme should be expanded and more effectively implemented.
E. Balanced Regional Development
- Targeted Investments in Underdeveloped Regions: Direct public and private investments towards less developed states and regions to stimulate economic growth and reduce regional disparities. Special economic zones (SEZs) and infrastructure development projects in these areas can attract businesses and create jobs.
- Decentralization of Economic Activities: Encourage the decentralization of economic activities by promoting growth in smaller cities and towns through urban planning and infrastructure development, thereby reducing the pressure on major urban centers and distributing economic benefits more evenly.
While India has achieved substantial economic growth, the widening gap between the rich and the poor remains a critical challenge. Addressing this issue requires comprehensive and inclusive policies that promote equitable distribution of wealth, ensure equal access to opportunities, and create sustainable livelihoods for all sections of society. By focusing on these measures, India can move towards a more balanced and just society where economic growth benefits everyone.
Check out UPSC Coaching Centre Guwahati | APSC Coaching Centre Guwahati | Crack APSC Exam | UPSC Civil Services Exam | Ethics Paper in UPSC Exams











