Understanding mountain systems is a core topic in geography for UPSC, APSC, and other competitive exams. Among all mountain types, young fold mountains hold special importance because they are geologically active and continuously evolving. Therefore, the question “Which Mountain is known as the Young Fold Mountain?” frequently appears in competitive exams.
The Himalayas Are Known as the Young Fold Mountains:
The Himalayas are known as the Young Fold Mountains of the world. They represent the youngest and most dynamically evolving mountain system on Earth. Moreover, they continue to rise even today due to ongoing tectonic movements. As a result, the Himalayas differ significantly from older mountain systems such as the Aravallis.
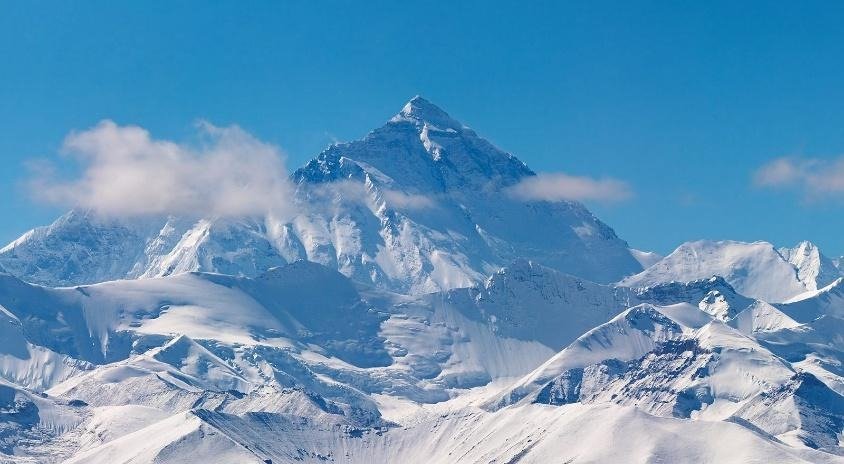

Why Are the Himalayas Called Young Fold Mountains?
- Recent Geological Origin: Firstly, the Himalayas formed during the Cenozoic Era, roughly 50 million years ago. In geological terms, this age is considered very recent. Therefore, geographers classify them as the ‘young mountain’.
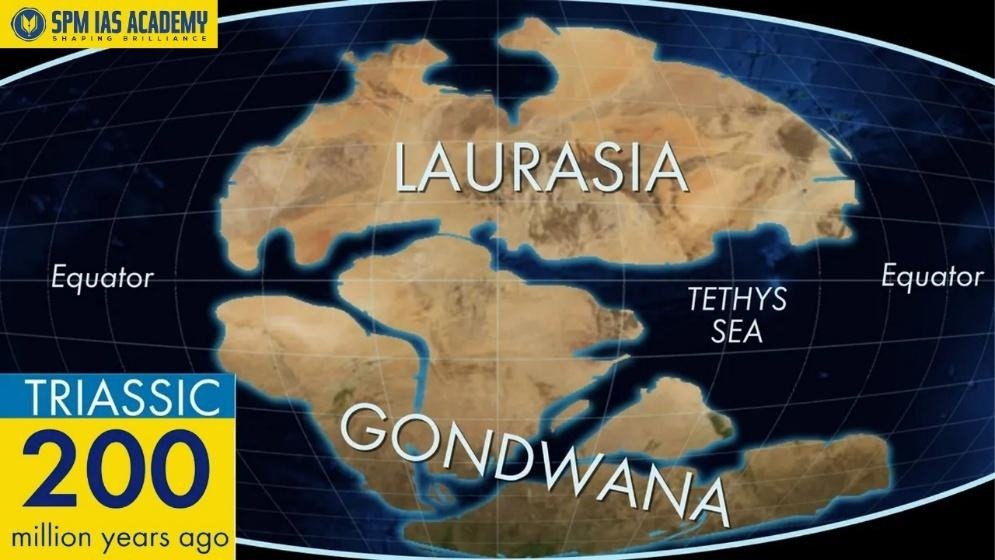
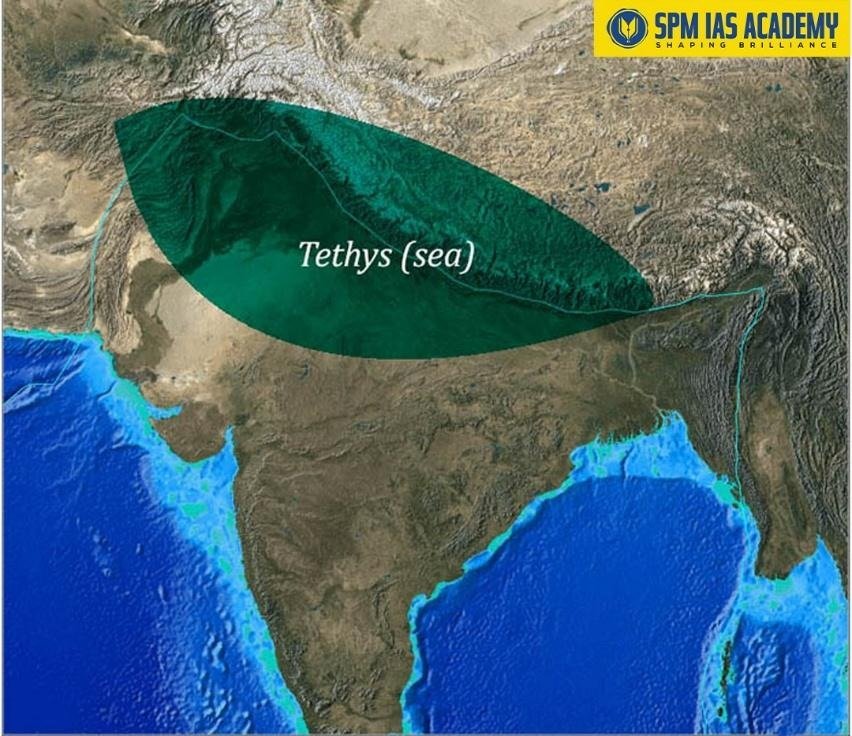
- Formation Through Folding: Secondly, the Himalayas formed due to folding of sedimentary rocks. These sediments accumulated in the ancient Tethys Sea. Later, tectonic forces compressed these layers and folded them into massive mountain chains.
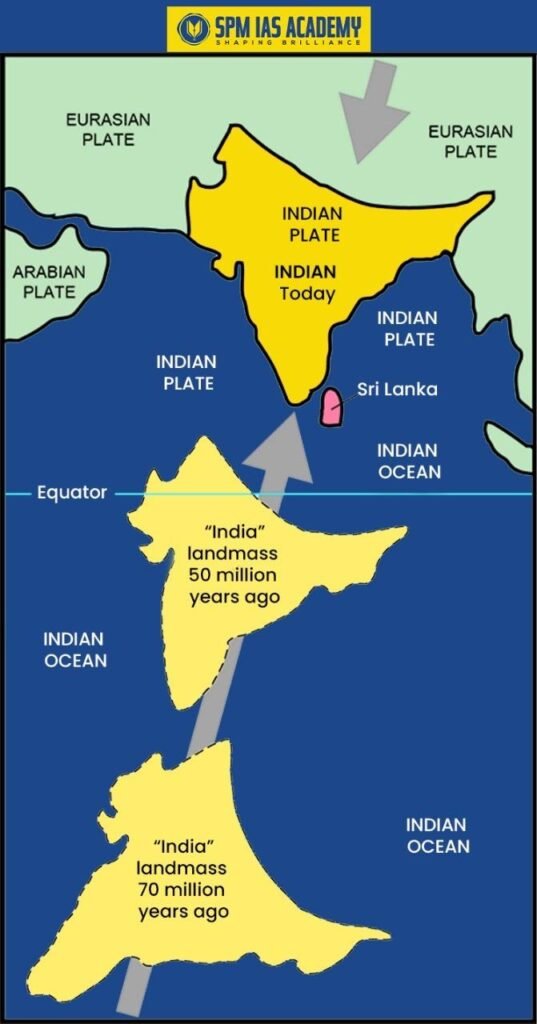
- Ongoing Tectonic Activity: Most importantly, the Himalayas are still rising. The Indian Plate continues to move northward and collide with the Eurasian Plate. Consequently, earthquakes and crustal uplift frequently occur in this region.
How Were the Himalayas Formed? (Plate Tectonic Explanation):
To understand young fold mountains clearly, one must examine plate tectonics.

- Initially, the Indian Plate drifted northward after separating from Gondwanaland.
- Meanwhile, the Eurasian Plate remained relatively stable.
- Eventually, both plates collided. As a result, the sediments of the Tethys Sea compressed and folded upward.
- Consequently, the Himalayan Mountain range emerged.
- Even today, this collision continues. Therefore, the Himalayas keep rising at a measurable rate.
Key Characteristics of Young Fold Mountains:
Young fold mountains share several distinct features. The Himalayas clearly display all of them.
- Highly Rugged Relief: Young fold mountains show steep slopes, sharp peaks, and deep valleys. The Himalayas exhibit dramatic topography, including some of the world’s highest peaks.
- Presence of Lofty Peaks: Mount Everest, Kanchenjunga, and Nanga Parbat rise within the Himalayan system. These peaks confirm the youthful nature of the range.
- High Seismic Activity: Because tectonic forces remain active, earthquakes frequently occur in Himalayan regions. Hence, this feature strongly supports their classification as young fold mountains.
- Deep Gorges and River Valleys: Rivers such as the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra cut deep gorges through the Himalayas. This vertical erosion indicates ongoing uplift.
Comparison – Young Fold Mountains vs Old Fold Mountains:
| Feature | Young Fold Mountains | Old Fold Mountains |
| Geological Age | Very recent (E.g. Tertiary period (Cenozoic era), around 50 million years ago) | Very old (Over 250 million years ago) |
| Height | High altitude | Low altitude |
| Slopes | Steep slopes and deep valleys | Gentle slopes and shallow valleys |
| Earthquake Activity | Active, still growing | Negligible, Inactive |
| Example | Himalayas, Alps, Andes | Aravalli Range, Urals, Appalachians |
Why the Himalayas Matter Geographically:
The Himalayas influence India and Asia in multiple ways.
- Climatic Role: Firstly, they act as a climatic barrier. They block cold Central Asian winds and force monsoon winds to shed rainfall over the Indian subcontinent.
- Source of Major Rivers: Secondly, they give rise to perennial rivers. These rivers support agriculture, drinking water supply, and hydroelectric power.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Moreover, the Himalayas host diverse flora and fauna across altitude zones.
- Strategic and Cultural Importance: Finally, the Himalayas hold immense strategic, cultural, and spiritual value for India and neighbouring countries.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Himalayas are known as the Young Fold Mountains of the world. They formed due to the collision of the Indian and Eurasian plates and continue to evolve even today. Because of their recent origin, folded structure, seismic activity, and towering peaks, geographers classify them as young fold mountains. For UPSC, APSC, and State PCS aspirants, this topic holds high conceptual and factual importance. Therefore, understanding it with tectonic reasoning ensures better answer quality in both prelims and mains.
Sources:
The Himalayas are known as the Young Fold Mountains because they formed recently in geological terms and are still rising due to active tectonic movements.
The Himalayas are called young fold mountains because they formed during the Cenozoic Era, through the folding of sedimentary rocks, and continue to experience tectonic uplift.
Young fold mountains were formed mainly during the Tertiary period of the Cenozoic Era, around 50 million years ago.
The collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate led to the formation of the Himalayas as young fold mountains.
Young fold mountains are prone to earthquakes because tectonic activity is still ongoing, causing frequent crustal movements and seismic disturbances.











