Why in the News?
India conducted its first flight tests of the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS). This took place off the coast of Odisha. The tests were successfully conducted under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
Introduction
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) conducted the first flight tests. Particularly, these tests were for the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS). Additionally, the tests were part of Mission Sudarshan Chakra. Moreover, this is a huge milestone for Indian air defence. Here, in this article, we will look into the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System and its components.
What is the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS)?
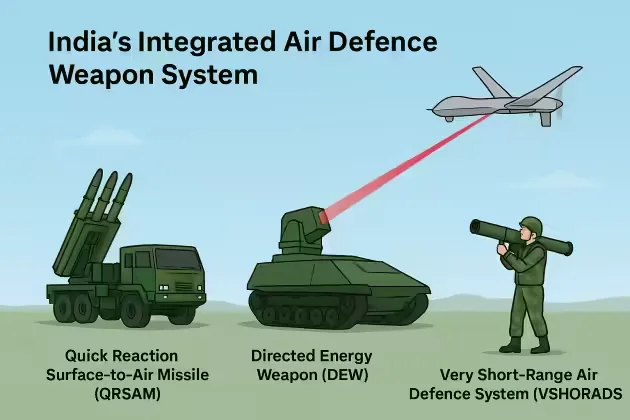
The Integrated Air Defence Weapon System is a multi-layered air defence system. Accordingly, this Indian air defence has three components:
- Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missiles (QRSAM)
- Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS) missiles
- High-power laser-based Directed Energy Weapon (DEW)
1. DRDO has developed and designed the QRSAM
2. VSHORADS is developed by the Research Centre Imarat (RCI).
3. DEW is developed by the Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences (CHESS).
4. Both RCI and CHESS are Hyderabad-based facilities of the DRDO.
Another key point is that the operation of all these weapon system components is integrated. Accordingly, the Centralised Command and Control Centre controls it. The Defence Research and Development Laboratory developed this centre in Hyderabad.
IADWS builds on India’s use of S-400, Barak-8, and Akash systems. During the “Operation Sindoor”, the Indian forces used these systems to intercept Pakistani drones and missiles.
What is the aim of the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System?
Below are the goals of the IADWS:
- To provide comprehensive protection for military and national assets. This includes airbases, radar sites, command centers, nuclear and space installations, and power plants.
- To counter modern aerial threats, we must address various challenges. These include high-speed aircraft and cruise missiles. Additionally, drones and swarm UAVs pose significant risks. Loitering munitions are also part of the equation.
How does the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System work?
1. Centralised Command & Control Centre (C2C2): Combines radar and electro-optical sensor data to create a real-time aerial situation display.
2. Threat Allocation: Based on the target’s speed, altitude, and trajectory, C2C2 assigns the most effective weapon.
- QRSAM (outer layer): Engages fast jets, helicopters, and cruise missiles at a range of 25 to 30 kilometers. It can reach an altitude of approximately 10 kilometers.
- VSHORADS (middle layer): The system is based on infrared guidance. It is effective against low-flying UAVs and helicopters. The range is up to 6 kilometers. It can target altitudes of up to 4 kilometers.
- DEW (inner layer): High-power lasers can neutralize drones and loitering munitions at close range. They are cost-effective and have unlimited firing capacity.
What is Mission Sudarshan Chakra?
Announced on the 79th Independence Day, it is a national security initiative. Mission Sudarshan Chakra aims to develop an indigenous Iron Dome-like air defence system. This Indian air defence system will feature advanced technologies and multi-layered defense mechanisms. The goal is to achieve the Iron Dome-like air defence system by 2035 to protect critical civil and defense infrastructure.
Mission Sudarshan Chakra aims to neutralize enemy attacks. It will enable swift counterstrikes, ensuring rapid and precise defense. Ultimately, this initiative seeks to strengthen India’s strategic autonomy and Indian air defence.
What are the Three Components of the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System?
The Integrated Air Defence Weapon System has three components. They are discussed in detail below:
1. Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missiles (QRSAM): In the first place, it is a short-range Surface to Air Missile (SAM) system. Moreover, the system, primarily designed to provide a protective shield, protects moving armoured columns of the Army from enemy aerial attacks.
- The entire weapon system is configured on highly mobile platforms. In addition, it has search and track capability. Further, the system can fire on short halts. It has an operational range of three to 30 kilometers.
- The QRSAM weapon ensemble consists of several components. It includes a fully automated command and control system.
- There are two types of radars: the Active Array Battery Surveillance Radar and the Active Array Battery Multifunction Radar. Both radars provide 360-degree coverage. They have capabilities for “search on move” and “track on move.” Additionally, there is one launcher in the ensemble.
2. Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS): This is a fourth-generation miniaturized Man Portable Air Defence System (MANPAD). The VSHORADS are technically advanced. This missile system can meet the needs of all three branches of the Armed Forces: the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
3. Directed Energy Weapon (DEW): Earlier this April, the CHESS facility conducted a successful field demonstration. Moreover, this demonstration featured the land version of the Vehicle-Mounted Laser DEW MK-II(A).
- The system defeated fixed-wing UAVs and swarm drones significantly.
- Correspondingly, it caused structural damage and disabled their surveillance sensors.
- Together with this achievement, India has joined an exclusive club of global powers that possess such a system.
- The DEW is said to have a range of less than three kilometers.
What are the Features of the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System?
Below are the primary features of IADWS:
1. Indigenous design: The IADWS is particularly designed with advanced radars, sensors, and communication systems.
2. Multi-layered shield: Furthermore, the multi-layered IADWS combines kinetic interceptors (missiles) and non-kinetic weapons (lasers).
3. Real-time coordination: Not to mention that the coordination timings of the IADWS are remarkable. Thus, this ensures simultaneous tracking and engagement of multiple targets.
4. Rapid reaction & mobility: Further, they help in deployment in forward areas.
5. Air defence system: In addition, area Defence for high-value facilities against diverse aerial threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS) represents a significant advancement in India’s air defense capabilities. Accordingly, the IADWS integrates modern technologies and multi-layered defense mechanisms. Thus, the IADWS enhances India’s readiness against different aerial threats.
Significantly, the flight tests conducted by DRDO under Mission Sudarshan Chakra were successful. Moreover, this demonstrates India’s commitment to self-reliance in its air defense system. They operate cohesively; hence, the IADWS aims to strengthen India’s national security and protect its vital infrastructure.
Also read: SUDARSHAN CHAKRA MISSION—INDIA’S SHIELD FOR 2035
Frequently Asked Questions
A: Reduced reliance on expensive ammunition and lower collateral damage.
A: Short-range air defense (SHORAD) is a group of anti-aircraft weapons and tactics designed to defend against low-altitude air threats.









