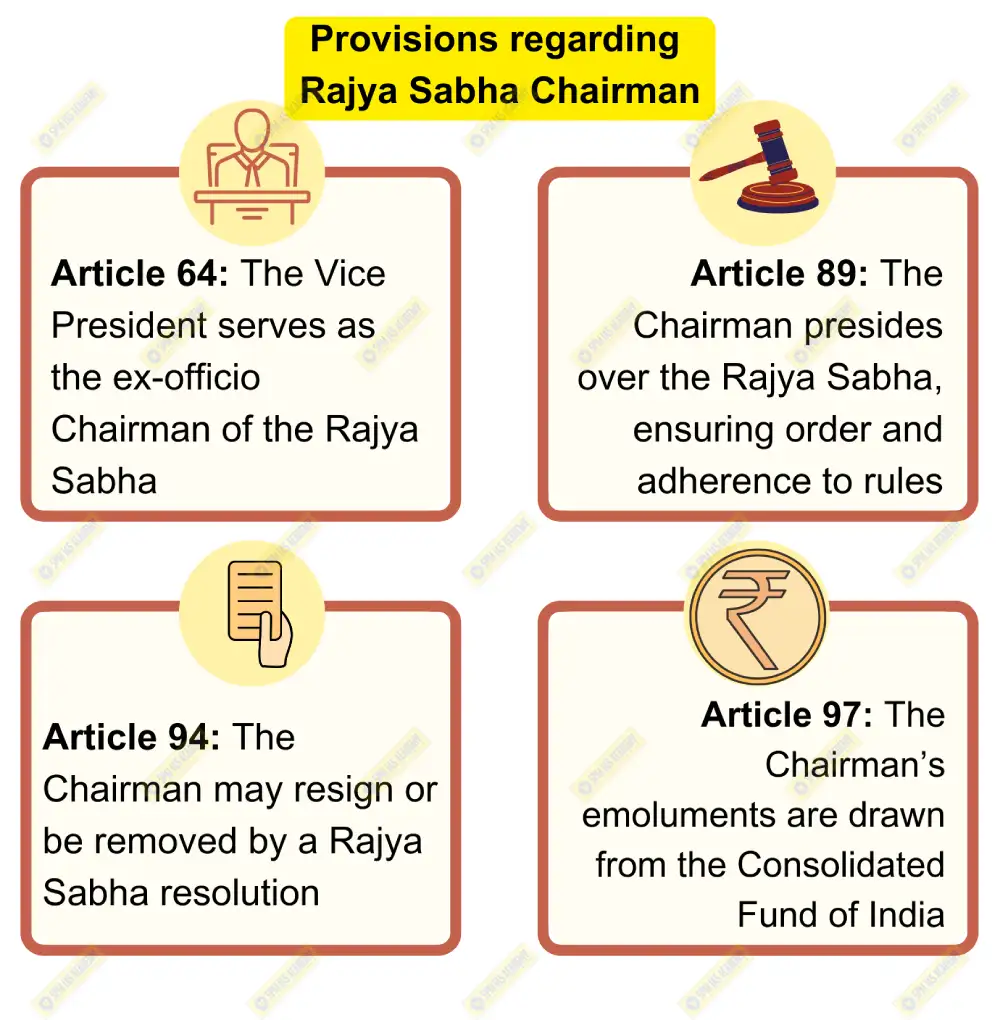
The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, as the presiding officer, holds a vital constitutional role as the guardian of the prestige and dignity of the House. The position, established under Article 89 of the Indian Constitution, assigns the Vice President of India as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, responsible for maintaining decorum, ensuring adherence to rules, and facilitating productive legislative discourse. This role is central to upholding the Rajya Sabha’s constitutional mandate as the “Council of States,” representing the interests of Indian states within the framework of parliamentary democracy.
Key Responsibilities of the Chairman in Guarding Prestige and Dignity
1. Maintenance of Order and Decorum:
- The Chairman has the power to regulate debates, manage disruptions, and ensure the House’s decorum. According to Article 118, Parliament is empowered to make its rules of procedure, with the Chairman entrusted to enforce these rules impartially in the Rajya Sabha.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar highlighted the necessity for discipline within legislative bodies to protect their efficiency, emphasizing that “disorder is a threat to the democratic process.” In line with Ambedkar’s views, the Chairman’s role in maintaining order is crucial to preserving the House’s integrity and effectiveness.
2. Impartiality and Fairness:
- As the custodian of the House’s dignity, the Chairman must act impartially, setting aside personal and political biases. Justice H.R. Khanna noted that the presiding officer should be “a symbol of impartiality and fairness,” a standard critical for fostering mutual respect and decorum within parliamentary proceedings.
- The Chairman’s impartial stance reinforces the trust and authority of the office, ensuring that all members, irrespective of party affiliation, receive fair treatment. The Rajya Sabha’s Rules of Procedure grant the Chairman authority to make final decisions on procedural matters, underscoring this impartial role.
3. Disciplinary Powers:
- The Chairman has significant powers to enforce discipline, including the authority to suspend members for unruly behavior under Rule 255 of the Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in the Rajya Sabha. This power serves as a deterrent to maintain decorum, which is essential for the House’s dignity.
- Nani Palkhivala, an eminent jurist, argued that “discipline in legislative assemblies is essential to the nation’s democratic health,” underlining the Chairman’s role in implementing discipline for maintaining the House’s respect and functional efficiency.
4. Protection of Parliamentary Privileges:
- The Chairman plays a crucial role in safeguarding the privileges and immunities granted to the Rajya Sabha under Articles 105 and 122, which protect parliamentary proceedings from judicial scrutiny and uphold members’ freedom of speech in the House. By safeguarding these privileges, the Chairman protects the House’s dignity and ensures that members can express state interests without undue external influence or fear.
- M.N. Kaul and S.L. Shakdher, constitutional scholars, have highlighted the Chairman’s duty to uphold parliamentary privileges as fundamental to preserving the House’s dignity, emphasizing that without such protection, the House cannot function freely or effectively.
5. Symbol of Federal Balance:
- The Rajya Sabha represents the federal structure of India, giving states a voice in the central legislature. The Chairman, as the head of this federal council, plays a vital role in protecting the rights of states, thereby upholding the prestige of the House in its federal function.
- Justice M. Hidayatullah observed that the Rajya Sabha “reflects the unity in diversity of India’s federalism,” and the Chairman’s role in facilitating balanced state representation further elevates the House’s stature within the democratic structure.
The Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, as the presiding officer, is entrusted with upholding the dignity and prestige of the House, an essential aspect of India’s parliamentary democracy. From maintaining decorum and impartiality to protecting privileges and ensuring fair state representation, the Chairman’s responsibilities are vital for the Rajya Sabha’s functionality and respect. As Dr. S. Radhakrishnan, former Vice President and Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, aptly said, “Parliament is not merely a law-making body but a deliberative one,” underscoring the Chairman’s role in fostering dignified, effective, and meaningful legislative discussions. The office of the Chairman thus serves as a bulwark of constitutional values, enabling the Rajya Sabha to fulfill its role with dignity and honor.