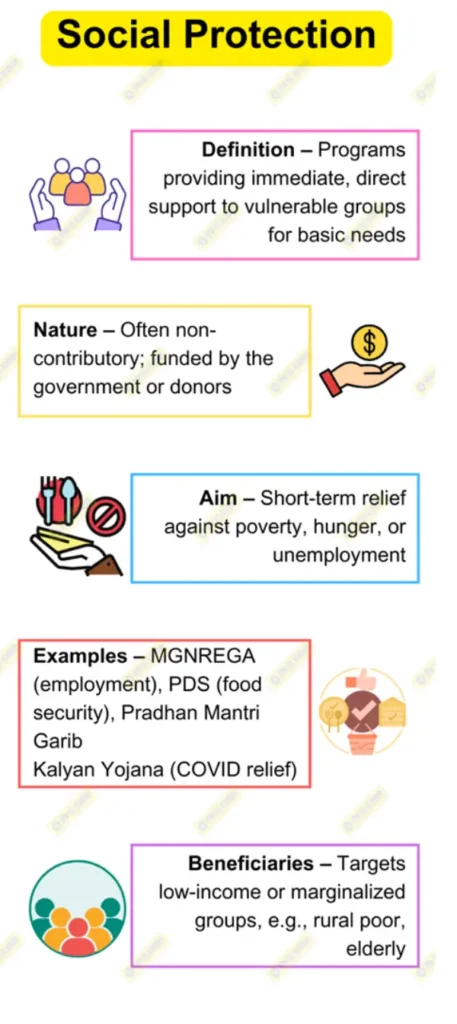
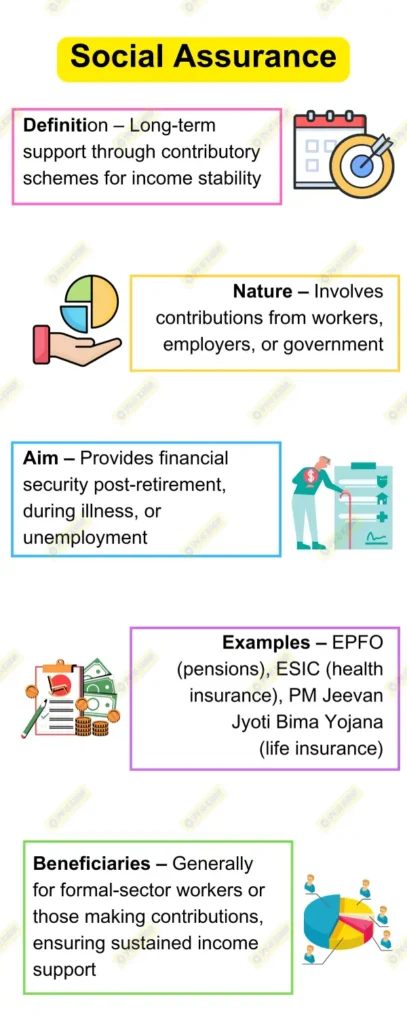
Social assistance and social insurance are two major components of social protection. Social assistance refers to non-contributory support provided to vulnerable populations, while social insurance is contributory, with beneficiaries receiving protection based on previous contributions, typically through schemes like pensions or health insurance. In developing economies, social assistance plays a more significant role because a large portion of the population works in the informal sector, which makes contributory schemes challenging to implement.
As Amartya Sen emphasizes, “Social security is a basic requirement for freedom,” underlining that social protection ensures basic welfare and dignity, especially for economically vulnerable populations. In this context, social assistance measures are essential for building a safety net in developing nations, where economic vulnerability is high and informal employment prevails.
Reasons for Higher Prevalence of Social Assistance in Developing Economies
1. Informal Sector and Low Contribution Capacity:
- In developing economies, such as India, over 80% of the workforce is in the informal sector (ILO 2021), with irregular incomes and no formal contracts, making contributory social insurance infeasible for most.
- As a result, governments implement social assistance schemes like Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY) and Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) to provide income security and job opportunities to those outside formal employment
2. Targeted Poverty Alleviation:
- Social assistance programs are designed to address immediate needs in vulnerable populations, reducing poverty and inequality. India’s Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY), which aims to provide affordable housing, and Orunodoi Scheme in Assam, which offers financial aid to vulnerable women, are examples of assistance-based schemes that provide direct support to improve living standards.
- According to NITI Aayog’s 2021 Multidimensional Poverty Index, social assistance has been instrumental in reducing poverty rates, with PMAY and MGNREGA cited as major contributors to declining poverty in rural areas.
3. Response to Economic Shocks:
- Social assistance measures provide an essential buffer during economic crises, pandemics, and natural disasters. During the COVID-19 pandemic, India expanded PMGKY and One Nation, One Ration Card initiatives, helping over 80 crore (800 million) people access food rations.
- These rapid-response social assistance measures are crucial in developing economies, where sudden economic disruptions can push millions back into poverty. According to World Bank 2021 data, approximately 30% of the world’s new poor are from South Asia, highlighting the need for immediate and flexible social support.
4. Resource Constraints and Scalability:
Social insurance programs, while beneficial, are costly and require consistent funding. Developing economies often lack the fiscal space to support large-scale contributory schemes, focusing instead on scalable social assistance. In India, PM-KISAN provides income support to small farmers, reaching over 10 crore (100 million) beneficiaries through direct transfers.
Key Social Assistance Initiatives in India
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): Provides at least 100 days of wage employment per year to rural households, addressing both income security and rural poverty.
- Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY): During COVID-19, it provided free food grains to millions, ensuring food security for the most vulnerable.
- National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP): Provides direct financial support to elderly, widowed, and disabled individuals below the poverty line, improving social equity.
Conclusion
In developing economies, social assistance measures are more prevalent and critical due to high levels of informality, poverty, and economic vulnerability. India’s approach to social protection, through schemes like MGNREGA, PM-KISAN, and PMGKY, illustrates how social assistance can be an effective tool in reducing poverty, ensuring food security, and stabilizing livelihoods. As economies grow and formalize, a gradual shift towards contributory social insurance can occur, but for now, social assistance remains indispensable for social protection in the developing world.