Environmental degradation refers to the deterioration of the environment through depletion of natural resources such as air, water, soil, and ecosystems. This degradation amplifies vulnerability to natural disasters by weakening ecosystems and reducing their capacity to buffer against hazards.
Causal Links
A. Deforestation and Flooding:
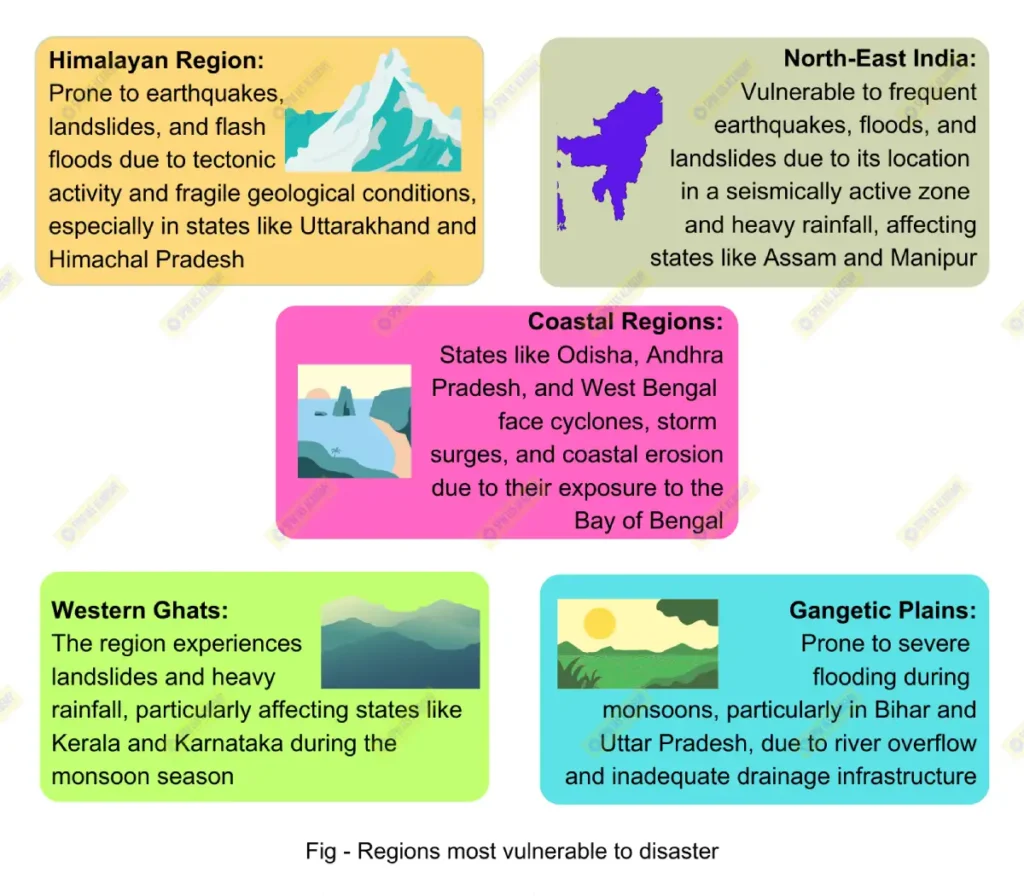
○ Trees and forests act as natural barriers to flooding by absorbing rainfall and stabilizing soil. The loss of forest cover increases runoff, causing floods. For example, the Uttarakhand floods of 2013 were exacerbated by extensive deforestation in the region, reducing the land’s ability to absorb water and causing landslides.
B. Soil Erosion and Landslides:
○ Unchecked deforestation, overgrazing, and unsustainable farming practices lead to soil erosion. This makes slopes vulnerable to landslides during heavy rains. The Kedarnath landslide during the 2013 Uttarakhand disaster is a stark reminder of how environmental degradation intensifies landslides.
C. Wetland Degradation and Storm Surges:
○ Wetlands act as natural buffers against storms by absorbing excess water. Their destruction, often due to urbanization, increases the impact of storm surges and coastal flooding. The loss of wetlands in New Orleans before Hurricane Katrina (2005) significantly worsened the flooding.
D. Climate Change and Extreme Weather:
○ Climate change, driven by human activities like fossil fuel burning and deforestation, is intensifying extreme weather events. Rising global temperatures have led to more frequent and severe cyclones, heatwaves, and droughts. For instance, Cyclone Amphan (2020) caused extensive damage in India and Bangladesh, with scientists linking its intensity to warming ocean temperatures due to climate change.

Steps to Minimize Environmental Degradation
- Afforestation and Reforestation:
○ Planting trees helps restore ecosystems and prevents soil erosion, flooding, and landslides. The Indian government’s Green India Mission aims to increase forest cover to sequester carbon and protect against environmental degradation. Increased forest cover can act as a buffer against disasters like floods and landslides. - Sustainable Land Management:
○ Practices such as terrace farming, agroforestry, and crop rotation can prevent soil erosion and promote soil health. Ethiopia’s Tigray Region has implemented sustainable land management practices to combat soil erosion, reducing vulnerability to droughts and landslides. - Wetland Restoration:
○ Wetlands provide protection against floods and storm surges. Restoring wetlands along coastlines can minimize the impacts of natural disasters. For example, after Hurricane Katrina, there has been a push to restore wetlands in the Mississippi Delta to mitigate future storm impacts. - Renewable Energy Transition:
○ Shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources like solar and wind can mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This can help reduce the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. India’s International Solar Alliance promotes solar energy globally, reducing reliance on carbon-heavy energy sources.
Environmental degradation exacerbates vulnerability to disasters by weakening natural ecosystems that provide protection against hazards. Reducing degradation through afforestation, sustainable land management, wetland restoration, and transitioning to renewable energy can mitigate these vulnerabilities, making societies more resilient to disasters. Major disasters like the Uttarakhand floods and Cyclone Amphan highlight the urgent need to address these causal links.
Check out UPSC Coaching Centre Guwahati | APSC Coaching Centre Guwahati | Crack APSC Exam | UPSC Civil Services Exam | Ethics Paper in UPSC Exams












