The National Logistics Policy (NLP), launched in 2022, aims to streamline India’s logistics sector by improving infrastructure, reducing costs, and enhancing efficiency. Its goal is to make India a globally competitive logistics hub and achieve a logistics cost target of 8% of GDP (from the current 13-14%) by 2030. Here’s an outline of its key components:
A. Vision and Objectives
- The NLP envisions creating a seamless multimodal logistics network that enhances ease of doing business and trade competitiveness.
- Its primary objective is to reduce logistics costs to single-digit levels by improving logistical efficiency and adopting a tech-driven approach.
- NITI Aayog has supported the policy, noting that a robust logistics sector can contribute an additional 5% to India’s GDP by improving efficiency and exports.
B. Key Components and Initiatives
- Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP): Integrates all digital services related to logistics on a single platform to facilitate real-time information sharing and improve coordination among stakeholders.
- Logistics Data Bank (LDB): A national database for tracking container movement to improve traceability and reduce delays at ports.
- Capacity Building: Training logistics professionals through initiatives such as the Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalaya in Vadodara, which offers specialized education in logistics and transportation.
C. Focus on Infrastructure Development
- The policy aligns with the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan, which envisions infrastructure expansion through multimodal connectivity involving road, rail, air, and waterways.
- Infrastructure development under NLP prioritizes industrial corridors, including the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) and the Eastern and Western Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFC), to ensure faster cargo movement and reduced transit costs.
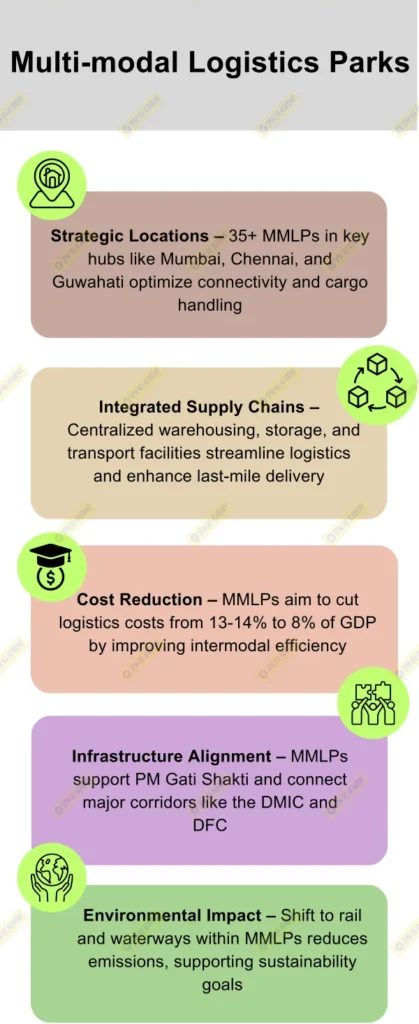
D. Promoting Multimodal Logistics Parks (MMLPs)
- Establishes 35+ Multimodal Logistics Parks across strategic locations like Mumbai, Chennai, Bengaluru, and Guwahati to integrate road, rail, air, and waterways, improving cargo handling and storage capabilities.
- These parks are expected to reduce costs by consolidating supply chains, improving warehousing standards, and facilitating intermodal transport.
E. Streamlined Regulatory Environment
- Introduces single-window clearances and regulatory reforms to streamline customs, warehousing, and clearance procedures for faster and transparent processes.
- The Suresh Prabhu Committee highlighted that bureaucratic delays and complex regulations add to logistics costs, underscoring the need for simplified policies.
F. Adoption of Technology and Digitization
- Encourages the use of drones, IoT, and blockchain to improve traceability, reduce manual intervention, and ensure paperless transactions.
- The ULIP platform integrates various ministries and logistic providers on a single digital interface, promoting transparency and reducing redundancies.
G. Environmental Sustainability
- Supports a shift to eco-friendly transportation modes, such as railways and inland waterways, to reduce carbon emissions.
- The NLP complements the National Green Hydrogen Mission by promoting hydrogen fuel in heavy-duty logistics vehicles to reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
The National Logistics Policy is a transformative step towards achieving a cost-efficient, tech-driven, and sustainable logistics ecosystem. By aligning with initiatives like PM Gati Shakti and Dedicated Freight Corridors, the NLP aims to make India a global logistics hub, reduce the cost of logistics, and boost economic growth by supporting seamless trade and supply chain management.