The Aravalli Mountain Range, one of the oldest in the world, stretches across northern India, impacting regions in Rajasthan, Haryana, Gujarat, and Delhi. Known for its rich geological history and ecological importance, the range also plays a significant role in India’s cultural and economic landscape. In recent years, however, the Aravalli Mountain ranges have been at the centre of various environmental and legal issues. For UPSC and APSC and other state PCS exam aspirants, it is crucial to understand not only the geographical and historical significance of the Aravallis but also the ongoing legal battles and challenges the range faces due to human activity.
This article provides a detailed exploration of the Aravalli Mountain Range, covering its geography, ecological importance, and recent legal issues affecting the region.
Why was the Aravalli Mountain range in the News?
- The Supreme Court has defined the Aravalli Mountain ranges uniformly.
- It has paused fresh mining leases across Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Gujarat. Furthermore, it has also issued directions for sustainable mining and ecological restoration of the region.
- Authorities must identify areas for mining and ecologically sensitive areas where mining is restricted.
What is the Supreme Court’s Definition of Aravalli Mountain Range?
- As per the new definition, Aravalli hills are any landforms with an elevation of 100 metres or more above local relief and will be recognized as part of the Aravalli range.
- Furthermore, an Aravalli Range is a collection of two or more such hills within 500 metres of each other.
- The new definition establishes clear boundaries for mining and conservation.
- Impact of the Ruling:
- The ruling has sparked outrage, with some calling it a ‘death warrant’ for the Aravallis.
- Environmental experts warn that the new definition could leave parts of the Aravallis unprotected.
- This could expose regions like Delhi to harsh weather and drought conditions.
- Public Outcry:
The ‘Save Aravalli’ campaign has gained momentum on social media. The new definition has triggered concern among environmental activists and experts. The Aravalli Mountain ranges are critical for the environment and there is a call for protection and restoration.
Geographical Distribution of the Aravalli Mountain Range:
The Aravalli Range runs for approximately 800 kilometres from northeast to southwest, acting as a geographical divide between the Thar Desert to the northwest and the fertile plains to the southeast. The range stretches across Rajasthan, Haryana, and Gujarat.
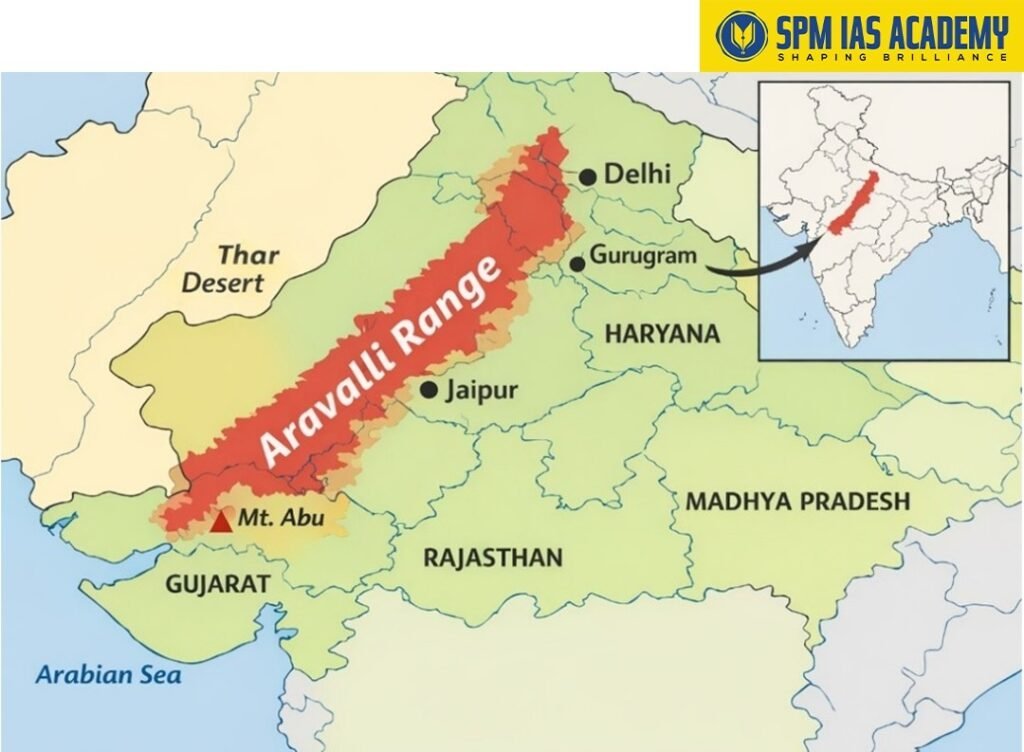
- Location and Extent:
The Aravalli Range begins near Delhi, extending through Haryana and Rajasthan, and eventually fades into the desert regions of Gujarat. The range significantly influences the climate and water systems of northern India. - Highest Peak – Guru Shikhar:
The highest point of the Aravalli Range is Guru Shikhar, located in Mount Abu, Rajasthan. It rises to 1,722 meters (5,650 feet) above sea level and is both a popular tourist and pilgrimage destination. - Physical Characteristics:
Unlike the Himalayas, the Aravalli Mountain ranges are much older and have been heavily eroded over billions of years, resulting in a more rounded and low-profile landscape. The range is made up of ancient metamorphic rocks such as granite, schists, and gneisses.
Ecological Importance of the Aravalli Range:
The Aravalli Mountain range plays a vital role in climate moderation, water conservation, and maintaining biodiversity in the region.
- Climate Regulation: Acting as a natural barrier, the Aravalli Range helps to regulate the monsoon winds. It influences the rainfall patterns in the surrounding regions. This helps mitigate the severity of heat in the Thar Desert and maintains moisture levels in areas of Rajasthan and Haryana.
- Water Resources: The Aravalli Mountain ranges are the source of several rivers, including the Luni and Sarasvati. These rivers are crucial for irrigation and drinking water in the surrounding regions. The range helps recharge groundwater and provides water for both rural and urban populations.
- Biodiversity: Despite the arid climate, the Aravallis support various ecosystems such as scrub forests, grasslands, and rocky terrains. Wildlife species like leopards, tigers, and numerous bird species call this range home. Several protected areas, such as the Sariska Tiger Reserve, lie within the Aravalli Mountain range.
- Forest Cover and Conservation: The range once had dense forests, but deforestation has reduced the forest cover. The remaining forests play a critical role in preventing soil erosion and maintaining the health of local ecosystems.
Geological Significance of the Aravalli Mountain Range:
The Aravalli Mountain ranges are one of the oldest mountain ranges on Earth formed during the ancient Proterozoic era.
- Ancient Rocks: The range is primarily composed of granite, schist, and gneiss, which have undergone immense tectonic activity. These ancient rocks tell the story of Earth’s early geological history.
- Erosion and Landscape Evolution: Over time, the range has been subject to intense erosion, creating a relatively low and rounded profile. Unlike younger ranges, the Aravalli Mountain ranges feature hills and valleys rather than towering peaks.
- Mineral Deposits: The Aravalli Mountain ranges are rich in minerals like marble, limestone, and mica. Mining these resources has been an economic activity in the region but also poses environmental challenges.
Historical and Cultural Significance of the Aravalli Mountain range:
Throughout history, the Aravalli Mountain ranges have provided a strategic defence-line and have been a cultural hub for the indigenous people of the region.
- Strategic Importance: The Aravallis acted as natural fortifications for various ancient kingdoms, including Rajput rulers, who built forts such as Kumbhalgarh Fort and Chittorgarh Fort in the region.
- Cultural Heritage: The region is rich in cultural heritage, with communities like the Meenas and Rajputs having lived in the Aravallis for centuries. The Dilwara Temples in Mount Abu are a prime example of the region’s architectural and cultural richness.
What are the Challenges Faced by the Aravalli Mountain Range?
Despite its importance, the Aravalli Mountain ranges face numerous challenges:
- Deforestation and Habitat Loss: Urbanization and illegal logging have led to the depletion of forest cover in the Aravallis. This has resulted in the loss of wildlife habitat and increased vulnerability to soil erosion.
- Mining and Over-extraction of Resources: The extraction of minerals such as granite, marble, and limestone has caused significant environmental degradation. Mining operations, especially unregulated ones, have exacerbated the erosion of the mountain range.
- Encroachment by Urban Development: Rapid urbanization in cities like Delhi and Gurgaon has led to the encroachment of Aravalli land for real estate development. This has further compromised the ecological integrity of the range and diminished its ability to regulate the climate.
Conclusion:
The Aravalli Mountain Range, with its rich geological history, ecological significance, and cultural heritage, is one of the most important natural features in India. However, recent environmental and legal challenges, such as illegal mining, deforestation, and urbanization, threaten its survival. Supreme Court rulings and state-level interventions highlight the importance of conserving this region for future generations. For UPSC and APSC aspirants, understanding the Aravalli Mountain range is significant in geography, environmental policy, and legal governance. It is essential for a comprehensive grasp of India’s natural resources and their management.
Sources:
- https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/energy-and-environment/supreme-court-accepts-centres-definition-of-aravali-hills-bans-grant-of-fresh-mining-leases/article70307837.ece
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/new-updates/save-aravalli-campaign-floods-x-why-has-the-supreme-courts-ruling-on-aravallis-mountain-range-triggered-an-alarm-and-why-experts-call-it-death-warrant-explained/articleshow/126088733.cms?from=mdr
- https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/centre-rejects-mining-push-charge-behind-aravalli-definition-asserts-no-relaxation-9860742
The Aravalli Mountain Range is important because it regulates climate, prevents desertification, supports biodiversity, and recharges groundwater in Rajasthan, Haryana, Delhi, and Gujarat.
The Aravalli Range is in the news due to the Supreme Court’s uniform definition of the Aravallis and its order to pause fresh mining leases while directing ecological restoration.
Guru Shikhar, located in Mount Abu, Rajasthan, is the highest peak of the Aravalli Range, with a height of 1,722 metres.
The Aravalli Mountains are among the oldest because they formed during the Proterozoic Era and have undergone extensive erosion over billions of years.
Major threats include illegal mining, deforestation, urban encroachment, and habitat loss, which weaken the range’s ecological and climatic functions.












