The Digital India Programme, also known as Digital India 2.0, is a flagship scheme of the Government of India. It was launched on 1 July 2015. Its main goal is to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
In order to achieve this, the initiative aims to provide citizens with electronic access to government services. As a result, it seeks to improve lives through the digital delivery of services. Additionally, the programme aims to expand the digital economy.
Digital India 2.0 focuses on several key areas. First, it aims to digitize government processes. Second, it seeks to create a unique digital identity, known as Aadhaar or e-Pramaan. Finally, it ensures that services are delivered online. This shift is intended to increase transparency and accountability within the system.
In this article, we will look into the Digital India key features.
What are the Features of Digital India?
The Digital India was launched on July 1, 2015. This initiative was introduced by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY). Its vision is to transform India into a digitally empowered society. Additionally, it aims to create a knowledge economy.
1. Broadband Highways: Building nationwide high-speed internet (optical fibre) networks in both rural and urban areas.
2. Universal Mobile Connectivity: Extending mobile network access to remote and underserved villages.
3. Public Internet Access: Expanding Common Service Centres (CSCs) and Post Offices as multi-service digital hubs for e-governance.
4. E-Governance (e-Kranti): Reforming government through technology with paperless governance and digital delivery of services (e.g., e-Hospital, e-Education).
5. Digital Identity (Aadhaar): Providing every citizen a unique biometric ID (Aadhaar) for efficient access to services.
6. Digital Payments: Promoting cashless transactions via UPI, BHIM, RuPay, Aadhaar-enabled payment systems (AePS), and other fintech solutions.
7. Smart Cities & IoT: Integrating technology into urban planning, utilities, and management in smart cities.
8. Electronics Manufacturing: Encouraging domestic electronics production (Make in India) to reduce imports.
9. IT for Jobs: Skill development initiatives (e.g., free IT training) to create employment opportunities in the IT sector.
10. Cyber Security & Digital Literacy: Initiatives like the Cyber Swachhta Kendra and Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA) to ensure cybersecurity and spread basic digital skills.
Follow Digital India updates, reforms, and government schemes through daily Current affairs for UPSC and APSC exams.
What are the Objectives of Digital India 2.0?
Digital India is a government initiative. Its primary goal is to empower citizens through technology. Additionally, it aims to improve access to essential services. The initiative focuses on enhancing infrastructure. Moreover, it emphasizes digital literacy and transparency. As a result, it seeks to create a more connected and efficient nation.
Below are the objectives of Digital India 2.0:
1. Digital Infrastructure as Core Utility: Provide high-speed internet to all citizens (especially in rural areas), ensure mobile connectivity, and secure digital identity (Aadhaar) for everyone.
2. Governance & Services on Demand: Make all government services available online. Promote e-Governance through platforms like UMANG and DigiLocker, enabling seamless transactions and transparency.
3. Digital Empowerment of Citizens: Enhance digital literacy (PMGDISHA targets one literate person per rural household, and provide digital resources in local languages while ensuring cybersecurity to build trust.
4. Digital Payments: Encourage cashless transactions using platforms like UPI, BHIM, and RuPay.
5. Smart Cities and Innovation: Foster technology-based urban development and smart infrastructure.
6. Startups and IT Growth: Promote startups, digital innovation, and employment opportunities in the IT sector.
What are the Nine Pillars of The Digital India Initiative?
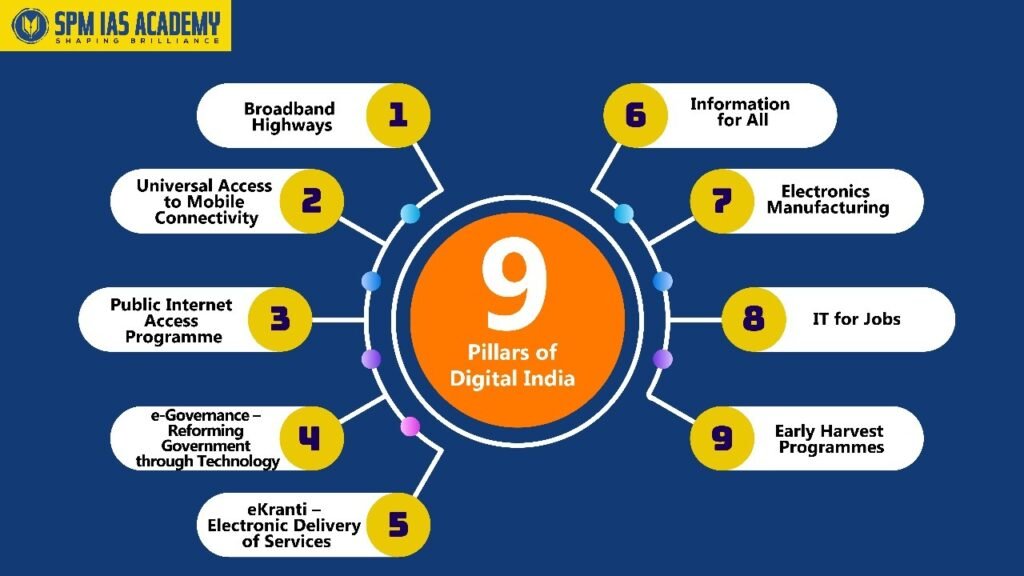
Digital India Initiative is built on nine pillars of growth. Below are the 9 nine pillars of Digital India:
- Broadband Highways – Building high-speed internet infrastructure nationwide.
- Universal Mobile Connectivity – Ensuring mobile access in all regions.
- Public Internet Access Programme – CSCs and digital kiosks in rural areas.
- e-Governance: Reforming Government through Technology – Paperless Offices and Online Services.
- e-Kranti: Electronic Delivery of Services – Digital delivery of government schemes and information.
- Information for All – Open data initiatives and proactive governance.
- Electronics Manufacturing – Promoting domestic production of electronics.
- IT for Jobs – Digital skill training and job creation in IT.
- Early Harvest Programmes – Quick-win projects like biometric attendance, Wi-Fi in universities, etc.
What are the Advantages/Impact of Digital India 2.0?
Below is a quick view of the Digital India 2.0 programme’s benefits:
| Advantage | Impact/Benefit of Digital India Programme |
| Connectivity | Broadband and mobile reach remote India (BharatNet) |
| E-Governance | Faster, transparent delivery of public services |
| Financial Inclusion | Cashless transactions (UPI, AePS) bring more people into banking |
| Digital Literacy & Skills | Large-scale IT training (PMGDISHA) empowers citizens |
| Economic Growth | Boost to e-commerce, startups, and IT jobs |
| Education & Healthcare | Online learning and telemedicine improve access |
| Innovation & Startups | Encourages entrepreneurship and tech innovation |
| Transparency | Digital records reduce corruption and increase accountability |
| Rural Empowerment | Focus on villages (internet, skills) to integrate rural areas |
| Global Leadership | India’s digital successes (like UPI scale) set global examples |
What are the Key Reforms of Digital India?
Digital India was launched in 2015. Its main goal is to empower society through enhanced digital infrastructure. Additionally, it aims to improve services and increase digital literacy. This initiative fosters economic growth and helps bridge the urban-rural divide. Overall, it seeks to create a more inclusive and connected society.
Below are the key reforms of Digital India:
1. Aadhaar: A biometric ID system providing unique 12-digit numbers for digital identity verification.
2. BharatNet: A broadband project enhancing digital connectivity in rural areas for e-governance and telemedicine.
3. Startup India: An initiative supporting innovation and tech startups with funding, mentorship, and incentives.
4. e-NAM: An online platform connecting agricultural markets to improve produce sales and farmer access to buyers.
5. Digital Locker: A secure cloud platform for storing and accessing essential documents, facilitating e-governance.
6. BHIM UPI: A mobile payment system enabling fast, secure peer-to-peer transactions via smartphones.
7. eSign Framework: An online tool for digitally signing documents using Aadhaar, ensuring paperless processes.
8. MyGov: A platform for citizen engagement in governance and policy discussions to promote transparency.
9. e-Hospital: A hospital management system for online appointments, e-records, and telemedicine services.
10. SWAYAM: A national MOOC platform offering free online courses for better education access and upskilling.
11. UMANG App: A mobile platform providing access to 1000+ government services for streamlined citizen interactions.
12. Smart Cities Mission: An initiative to improve urban services using ICT and IoT for better city management.
13. Digital India Act, 2023: A proposal to update the IT Act for regulating emerging tech and enhancing cybersecurity.
Conclusion
The Digital India Programme has transformed governance and the economy. It has enhanced connectivity, financial inclusion, and digital literacy. However, there are challenges, such as the digital divide. Despite these challenges, the programme’s impact on transparency and empowerment has been significant. Ultimately, it has made India more digitally inclusive.
UPSC & APSC Coaching in Guwahati provides expert guidance on governance initiatives like Digital India for competitive exam success.
Frequently Asked Questions
The Digital India launch date is 1 July 2015, and the nodal ministry isthe Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY).
They include Broadband Highways, Universal Mobile Connectivity, Public Internet Access (CSCs), e-Governance, e-Kranti, Information for All, Electronics Manufacturing, IT for Jobs, and Early Harvest Programmes.
The Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan trains one person per rural household in basic IT. It targeted 60 million learners, and by March 2024, had trained 63.9 million rural citizens.
Digital India is a key governance and economy topic for digital India UPSC. Questions have been asked about its pillars, objectives, and related schemes. For example, UPSC Prelims 2018 tested its aims (connect villages via Wi-Fi), and 2024 asked about Digital India’s land records programme.
In January 2025, the government launched National Broadband Mission 2.0 to accelerate the expansion of high-speed internet nationwide, complementing the BharatNet project for villages.












