“In this global milieu, the Indian economy remains a key driver of global growth. Growth momentum is buoyed by strong domestic growth drivers, sound macroeconomic fundamentals, and prudent policies.”
~ Sanjay Malhotra, RBI Governor
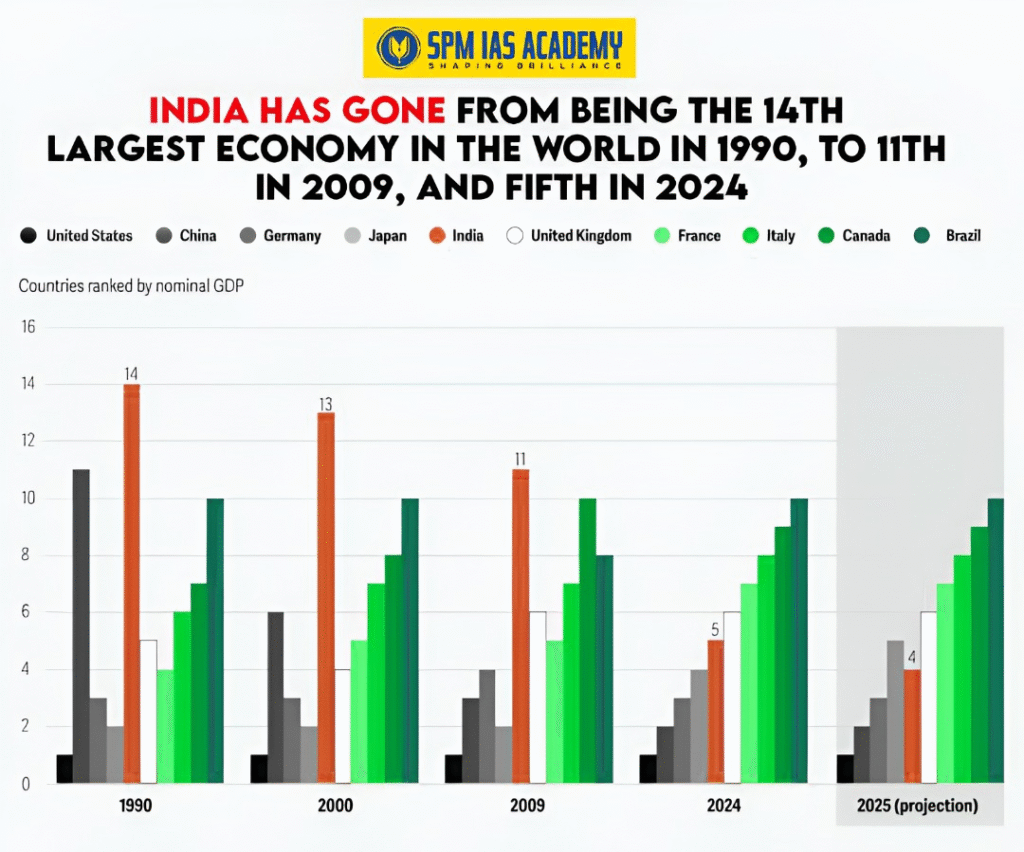
India’s Economic Surge
With a GDP growth rate of 7.4%, India is now the fastest-growing major economy in the world. The country’s strong growth story draws global attention, backed by solid economic foundations and steady performance. This ongoing progress comes from growing domestic demand, better rural consumption, increased urban spending, and a consistent rise in private investment.
Also read: UPSC Mains Result Out
GDP of Indian States:
India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is an important measure of the country’s economic health and growth. It significantly influences government policies, attracts investments, creates jobs, and raises the overall standard of living.
In 2025, Maharashtra holds the highest GDP among 34 Indian states and union territories, followed by Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, and Gujarat.
What is GDP?
GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product, which is the total value of all goods and services produced in a country over a specific period. GDP serves as a main indicator of the economic strength of a country as a whole. Generally, the technical term used for the GDP of Indian States is Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP)
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, Government of India, through the National Statistical Office (NSO), is the main authority in charge of calculating GDP and GSDP.
List of Top 10 Indian States by GDP 2025
India’s economic growth is constantly rising; the country will remain the world’s fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, having recently surpassed Japan. India’s total GDP is roughly $4.19 trillion, and its economic performance is characterized by the growth of the GDP of the indian states.
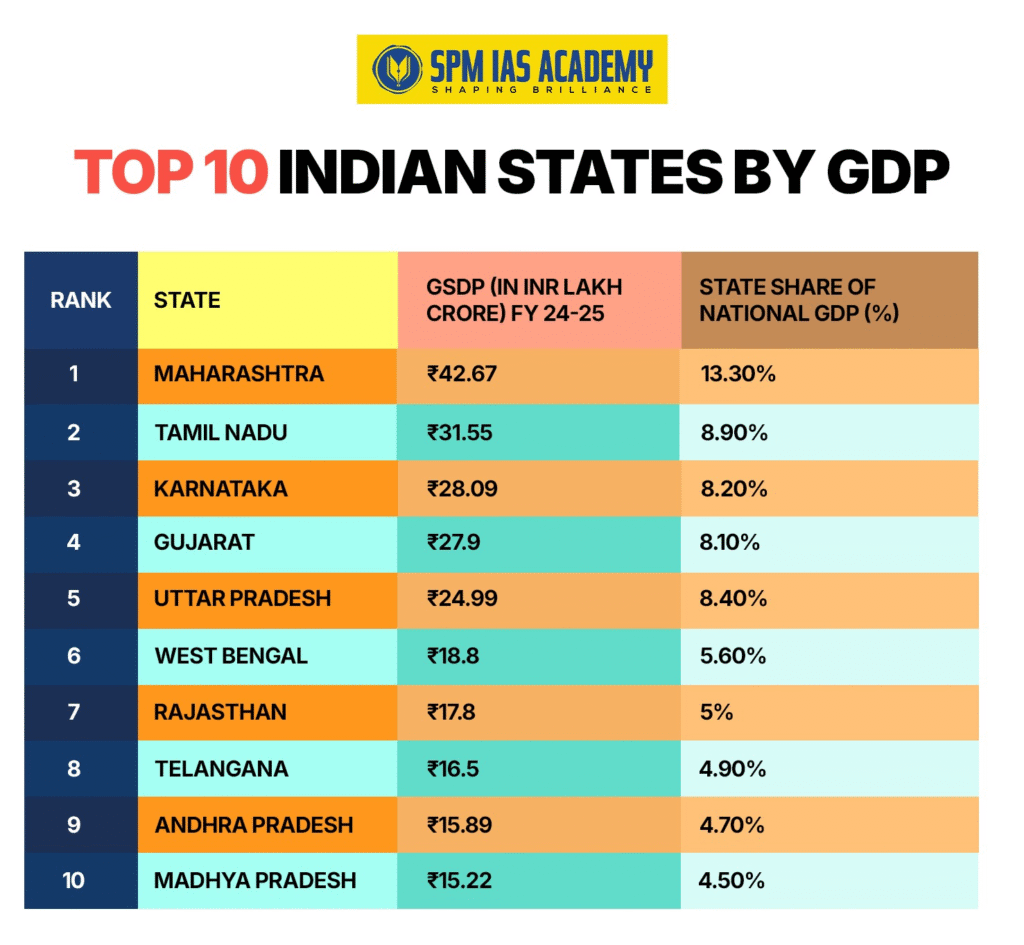
The top 5 states (Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, and Gujarat) alone share 47.71% of India’s total economy. Below is the list of top-performing states in terms of GDP.
Top 10 Indian States by GDP:
| Rank | State | GSDP ( in INR Lakh crore), FY 24-25 | State Share of National GDP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maharashtra | 42.67 | 13.30% |
| 2 | Tamil Nadu | 31.55 | 8.90% |
| 3 | Karnataka | 28.09 | 8.20% |
| 4 | Gujarat | 27.9 | 8.10% |
| 5 | Uttar Pradesh | 24.99 | 8.40% |
| 6 | West Bengal | 18.8 | 5.60% |
| 7 | Rajasthan | 17.8 | 5% |
| 8 | Telangana | 16.5 | 4.90% |
| 9 | Andhra Pradesh | 15.89 | 4.70% |
| 10 | Madhya Pradesh | 15.22 | 4.50% |
Maharashtra ranks as the top GSDP state in India due to its diverse and strong economy, robust growth in the industrial sector, IT sector, and agricultural sector. Other key factors include an attractive business climate, strong infrastructure, foreign direct investment, and a strong manufacturing and services sector.
State-wise GDP Of India 2025
The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) is the summation of the value of all goods and services produced during a year within a state. Analyzing India’s state-wise GSDP is useful to compare regions in terms of economic strength, growth, and development of a state. GSDP rankings of states highlight the wide-ranging economies from massively industrialized states to economies that depend on agriculture.
Below is the list of the growth rates of the GDP of indian states:
| State | GSDP (Cr INR at current prices) 24-25 |
| Maharashtra | 4,531,518 |
| Tamil Nadu | 3,118,590 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 2,978,224 |
| Karnataka | 2,883,903 |
| Gujarat | _ |
| West Bengal | 1,815,010 |
| Rajasthan | 1,704,339 |
| Telangana | 1,640,901 |
| Andhra Pradesh | 1,593,062 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 1,503,395 |
| Kerala | 1,248,533 |
| Delhi | 1,215,003 |
| Haryana | 1,213,951 |
| Bihar | 991,997 |
| Odisha | 890,038 |
| Punjab | 838,637 |
| Assam | 643,667 |
| Chhattisgarh | 567,880 |
| Jharkhand | 516,225 |
| Uttarakhand | 378,245 |
| Jammu & Kashmir | 262,458 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 231,690 |
| Goa | – |
| Tripura | 89,682 |
| Chandigarh | – |
| Meghalaya | 59,626 |
| Sikkim | – |
| Puducherry | 52,163 |
| Manipur | – |
| Nagaland | – |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 44,229 |
| Mizoram | – |
| Andaman & Nicobar Islands | – |
| Ladakh | – |
From these facts, it is seen that India’s largest state, Rajasthan, is at number 7, and the capital, Delhi, is at number 12. Five states of South India together account for 31% of India’s GDP. And the Northeast states’ GSDP counts for 3.01% of India’s total GDP.
GDP Per Capita Income of Indian States 2025:
As a whole, The Economic performance of each of the Indian states contributes differently to the growth of the nation. India’s economy is highly diversified with significant growth in the IT sector, the agriculture sector, and the service sector. The image of GDP per capita income of Indian states indicates the strength of the state’s economy, the level of development, and also the living standards of people.
State-Level Economic Growth and Future Growth Projections and Target for $1 Trillion Economy
India’s economic expansion is not merely fueled by the country as a whole, but by the increasing contributions from individual states. States in India are also now increasing their capacity to achieve a trillion-dollar economy status.
Below is the table of the Indian states’ Economic Ranking to achieve the target of $ 1 trillion economy goal.
| State | Current GDP (in $ billion) | Target Year for $1 trillion economy |
| Maharashtra | 500-550 | 2027-2028 |
| Tamil Nadu | 320-350 | 2030 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 250-300 | 2028-2029 |
| Karnataka | 250-280 | 2032 |
| Gujarat | 340-345 | 2030 |
| Telangana | 200 | 2034-2035 |
States like Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Karnataka are emerging as leaders in lifting India’s economy to become a 5-trillion-dollar economy.
India’s 5-trillion-dollar economy target:
History reminds us that great economies are not built in calm waters. Great economies are built in turbulent seas. India aims to reach a $5 trillion economy by 2027 and seeks to become the world’s third-largest economy. This vision reflects not just a significant change or small progress. It emphasizes not only growth, but also inclusive, sustainable, and honest growth. The key pillars guiding this transformation are Seva (Service), Sushan (Good Governance), and Navachar (Innovation).
Challenges in GDP Growth across Indian States
The economic growth of Indian states is not uniform. Each state has unique opportunities and challenges that impact its contribution to the national economy. Some states are improving in infrastructure, education, and technology, while others show a slowdown in the industrial, agricultural, service, IT, and manufacturing sectors. To know the major challenges in GDP growth across indian states, it is important to understand the key challenges which is hindering in growth of GDP across Indian states.
Some of the key challenges of GDP growth across Indian states are discussed below:
Challenges in the Indian Industrial Sectors:
The industrial sector functions as the backbone of economic development, and industrialization plays a vital role in transforming India into a global economic superpower. Industrial development across the states has been uneven; there are a few states, such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu, that are dominant in industrialisation and the manufacturing industry, while many other states are lagging behind, possessing old technology, limited investment, delayed policy implementation, poor logistics, and power supply issues that limit the potential for industry to expand.
What is industrial development?
Industrial development refers to the development and growth of industries within a region or nation for the purpose of promoting economic advancement, increasing employment, improving infrastructure, and increasing the supply of goods and services. Industrial development is important for modernization, technological change, and overall economic growth.
Major Problems of the Industrial Sector in Indian States:
a)Inadequate Infrastructure:
- Outdated infrastructure in roads, railways, and ports causes high transportation costs and delays by affecting industrial efficiency.
- Power Supply and Water Scarcity Issue- Frequent power cuts, high electricity cost, and insufficient water supply in sectors like textile and food processing hamper in progress of industries.
b)Skilled Labour Shortage:
- Skill Gap- The pace of technological change in manufacturing, IT, and services is fast. Many workers do not possess the advanced skills required to keep pace.
- Education Mismatch – Outdated traditional education systems and insufficient vocational training often fail to meet the demands of modern industries.
c)Environmental Sustainability:
- Climate Change– industries must adopt climate-friendly technologies and practices to promote sustainable developmental growth, but the high cost of green technologies hampers this initiative.
- Pollution and Environmental Impact– Rapid Industrialisation causes environmental degradation, causing air and water pollution, as well as hazardous waste from industries remains a major environmental challenge.
2) Challenges in the Agriculture Sectors in India:
The Indian agriculture sector contributed approximately 17.7% to India’s GDP in the fiscal year 2023–24. Agriculture contributes to both GDP and employment generation. States like Punjab and Haryana are leaders in India’s agriculture sector, especially for foodgrain production, with Punjab often called the “Granary of India”. However, many states in India are facing challenges such as outdated methods of farming, low productivity, inadequate irrigation, and erratic markets. These challenges can hinder GDP growth and rural development. Addressing the issues of agriculture is necessary to achieve sustainable economic growth and food security in the nation.
Major Problems of the Agriculture Sector in India:
a) Lack of modern technology :
- Traditional farming:In India, many farmers continue to rely on age-old agricultural practices, while the adoption of modern technologies has been relatively gradual. Limited awareness, challenges in accessing technology, and affordability issues often slow down the transition.
- Subsidies and Training: The government could support farmers by providing subsidies for modern machinery such as tractors, seed drills, and drones, along with training programs to help them effectively use these technologies, as access and familiarity with such tools remain limited for many.
b)Dependence on Monsoon:
- Rain Factor: Approximately 60% of farmland in India relies solely on the monsoons for its various phases of farming. Monsoon droughts or excessive rain result in crop failure and can lead to a financial burden to the farmer.
- Infrastructure Factor: The lack of proper infrastructure in irrigation, storage, transport, technology, and finance is one of the biggest obstacles to agricultural growth in Indian states..
c) Climate Change Impact:
- Global Warming: Temperatures across India have risen, increasing heat stress and reducing yields for heat-sensitive crops like wheat, chickpea, and some pulses.
- Adverse Climatic Condition: Unfavourable climatic conditions like floods, drought, cyclones, hailstorms, etc, negatively affect farming activities, crop production. These conditions disturb the natural growth cycle of crops and reduce overall productivity.
Strategies to Achieve $1 Trillion GDP Target of Indian States:
Several states, including Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka, have set a target of achieving a $1 trillion GDP within the next decade. They are focusing on strategic planning, infrastructure development, industrial growth, and innovation-driven policies to enhance economic productivity, attract investments, and create employment opportunities. This approach provides a framework to foster regional economic growth and long-term prosperity.
Here are some of the strategies of Indian States:
1) Strengthening the Manufacturing and Industrial Sector:
Boosting the manufacturing and industrial sector is key for Indian states aiming for $1 trillion GDP. This involves modernizing infrastructure, promoting MSMEs, attracting domestic and foreign investments, enhancing skill development, adopting advanced technologies, and ensuring ease of doing business.
2. Boosting the Agricultural Sector:
Key strategies to achieve a $1 trillion economy include adopting modern farming techniques, improving irrigation and water management, promoting high-yield and climate-resilient crops, enhancing cold storage and supply chains, supporting agritech innovations, ensuring fair market access, and providing financial assistance to farmers. Targeted investments in rural infrastructure and sustainable agricultural practices can boost productivity, create employment opportunities, and make a substantial contribution to both state and national economic growth.
3) Expanding the Services Sector
To boost GDP, Indian states must focus on expanding IT, finance, tourism, healthcare, and education services. Key strategies include improving digital infrastructure, promoting startups, enhancing skill development, attracting foreign investment, and creating business-friendly policies. Encouraging innovation, simplifying regulations, and investing in quality human capital will make the service sector a major driver of economic growth.
Conclusion:
Understanding the GDP of Indian states in 2025 provides valuable insights into the economic landscape of the country. From industrial hubs to emerging markets, state-wise GDP and GDP per capita rankings highlight regional growth patterns, investment opportunities, and development potential. Tracking these trends helps policymakers, investors, and businesses make informed decisions.
Latest Articles
| Article Title | Read More |
|---|---|
| Top 10 UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India | Read Article |
| Special Agencies of United Nations | Read Article |
| Tiger Reserves in India | Read Article |
| Neighboring Countries of India | Read Article |
| Middle East Countries | Read Article |
| Top 10 Highest Mountain Peaks in India | Read Article |
| 10 Most Powerful Countries in the World by Military Strength | Read Article |
FAQ: GDP of Indian States 2025
India is on track to become the 4th largest economy globally by surpassing Japan with a GDP of $4.19 trillion.
Maharashtra continues to hold the top position in 2025 with the highest GDP among Indian states.
Goa ranks highest in GDP per capita in 2025, indicating strong economic productivity relative to its population size.
Total GDP measures the overall economic output of a state, while GDP per capita divides this output by the population, showing the average economic wealth per person.
Key contributors include industrial development, IT and service sectors, agriculture productivity, manufacturing output, and investments in infrastructure.












