Why in the News?
The Inner Line Permit (ILP) system in Arunachal Pradesh is witnessing a major digital transformation. The State government has announced a fully digitised ILP platform, which is expected to strengthen monitoring, enhance transparency and protect the indigenous communities of the State.
This article explains the evolution, significance, challenges and recent digital reforms of the ILP system.
What Is the Inner Line Permit (ILP) System?
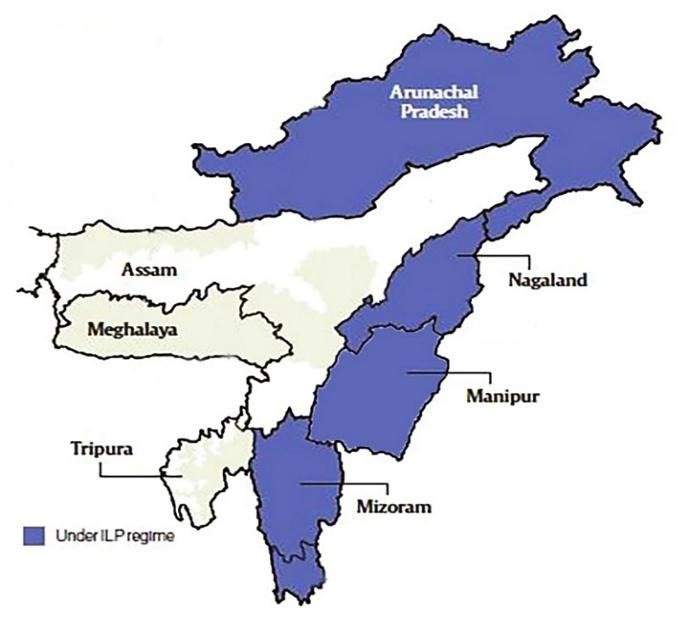
- The Inner Line Permit (ILP) is an official travel document required by non-residents, including Indian citizens from outside Arunachal Pradesh, to enter the State.
- It was issued under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation (BEFR), 1873.
- During the British period, under Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873, the British govt. followed ‘Isolationist Policy’ of not interfering with a tribe’s internal affairs.
- The Foreigners (Protected Areas) Order, 1958 defines the ‘Inner Line’ throughout India starting from Jammu and Kashmir and ending in Mizoram. A traveller needs ILP to visit beyond this line.
- Under the Order of 1958, all areas falling between the ‘Inner Line’ and the ‘International Border of the State’ are ‘Protected Area’. Whereas, areas falling between the ‘Inner Line’ and the ‘Territory occupied by indigenous tribes’ are ‘Restricted Area’, which are prohibited for entry without a permit.
- ILP is an official document issued by the government of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram which allows travel into a protected or restricted area for a certain period of time.
- The ILP system aims to:
- Regulate the entry of visitors.
- Protect tribal land rights.
- Preserve indigenous identity of tribes living in restricted areas.
- Prevent illegal settlement and demographic changes, preserving the rich heritage of the Northeastern tribes.
- Protection of their religious, social and customary laws, ownership and transfer of land.
- Ensure administration of civil and criminal justice.
Who can obtain the Inner Line Permit?
- The Inner Line Permit could be availed by both domestic as well as foreign tourists.
- For a domestic tourist, the permit is known as the ‘Inner Line Permit’. This would avail him movement in all of the “restricted” and “protected” areas of Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur and Mizoram.
- For foreign tourist (except a tourist of Bhutan) the permit is known as the ‘Protected Area Permit’ which is similar to that of the Inner Line Permit.
Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873 (BEFR)
- The first administrative policy of the British in the North-East India was the introduction of Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation in 1873. It was also known as the Inner Line Regulation.
- The Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873 is the legal basis for ILP system. The BEFR Act, 1873 empowers the State to control the movement of outsiders.
- It provides legal safeguards for tribal belts and protects their socio-cultural structure.
- Under Section 2 of the Regulation an “inner line” was prescribed by the state authority for limiting movement.
- Section 4 gave the state authority power to provide a permit for passing or residing in any of these “inner line” areas.
- The idea behind this regulation was to protect the culture and identity of indigenous tribes in the region. It also provides them some autonomy to look into their personal tribal affairs.
- For UPSC and APPSC exams, understanding BEFR is vital because it links to:
- Federalism
- Tribal rights and autonomy
- Special constitutional protections in Northeast India
- Internal security and migration issues
Why Is the ILP System Important for Arunachal Pradesh?
The ILP system acts as a protective shield for the State. It –
- Safeguards indigenous communities and their cultural identity.
- Regulates movement of migrant workers and visitors.
- Protects sensitive border regions near China.
- Prevents illegal land transactions.
- Controls overstaying and unauthorised settlements.
For Northeast India, the ILP also strengthens strategic stability and internal security.
Arunachal Pradesh Launches Fully Digital ILP System:
The State government is implementing the biggest-ever upgrade of its ILP system.
The digital overhaul has been under development for nearly three years and is now entering its final phase.
Key Features of the Digital ILP Overhaul:
- Real-time digital records of all visitors.
- Identification of overstaying ILP holders.
- Automated verification and monitoring.
- Backend integration completed by technology partners.
- Expected launch within the next few months.
- Enhanced coordination between enforcement agencies.
These features will significantly improve migration governance, accountability, and security vigilance.
Rising ILP Violations and the Need for Stronger Enforcement:
Arunachal Pradesh recorded around 5,000 ILP violations between January and November in 2025. Authorities conducted intensive ILP checks across districts to detect illegal entry and overstaying.
The new digital platform will now track:
- Every issued permit
- Entry and exit logs
- Overstay duration
- Repeat offenders
Therefore, the system will ensure robust monitoring, fool-proof tracking, and quick enforcement.
Issue of Illegal Migration – Government’s Stand:
- Chief Minister Pema Khandu highlighted concerns regarding illegal Bangladeshi nationals entering the State.
- He urged citizens not to panic due to unverified social media claims.
- However, he assured strict verification and enforcement. The digital ILP mechanism will help authorities tighten control over illegal entry routes and unauthorised settlements.
Benefits of the Digital ILP System:
- Better Monitoring and Transparency: Real-time tracking ensures accurate data on the movement of visitors.
- Strengthened Indigenous Rights: The system preserves tribal culture and traditional land ownership.
- Enhanced Internal Security: It improves surveillance over border movement and migrant labour.
- Improved Governance Efficiency: Digitisation reduces manual errors, delays and manipulation.
- Boost to Tourism with Regulated Access: Streamlined entry encourages responsible tourism without risking local demography.
Challenges Related to ILP System:
- Balancing development with protective regulations.
- Preventing misuse by political or interest groups.
- Addressing illegal migration along porous borders.
- Ensuring digital access in remote districts.
- Maintaining data privacy and cybersecurity.
ILP and National Security Concerns
Arunachal Pradesh shares a long and sensitive border with China (Tibet).
Hence, strict movement regulation is vital to:
- Prevent infiltration
- Monitor labour movement near strategic zones
- Support counter-insurgency efforts
- Protect vulnerable tribal communities in border villages
This adds a Geopolitical and Internal Security angle for UPSC GS Paper 3.
Criticism of the Inner Line Permit (ILP) System:
- Colonial Legacy & Purpose:
- Originally introduced by the British to enforce an isolationist policy, maintain strategic control, and facilitate commercial interests such as plantation expansion.
- Designed more for administrative convenience than for long-term socio-economic development.
- Impact on Tourism:
- The ILP acts as a regulatory barrier, restricting the flow of tourists into the region.
- Reduced tourist footfall affects livelihood opportunities in a region where tourism is a key economic driver.
- Some states like Arunachal Pradesh have attempted reforms through e-ILP systems to simplify the process.
- Impact on Economy:
- ILP is perceived as counterproductive to social integration, economic development, and technological advancement of the region.
- It restricts entry even for people from other North-Eastern states, limiting the movement of labourers, small traders, and service providers.
- This affects access to local markets, coalfields, construction sites, and other essential livelihood zones.
- The restrictive regime discourages private investment, slowing industrial and infrastructural growth.
- Illegal Migration Concerns:
- Despite ILP enforcement, illegal migration continues to be a major challenge in several northeastern states.
- Weak implementation and porous borders undermine the intended objective of the ILP in preventing demographic changes.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Digital Infrastructure: Remote districts need stable internet and trained staff.
- Increase Awareness: Travellers must understand ILP rules and penalties.
- Regular Audits: Monitoring systems require periodic review for accuracy.
- Coordination With Border Forces: Integrated ILP data must support security agencies.
- Balanced Development Approach: Protection of tribal identity must coexist with tourism and economic growth.
Conclusion:
The digital overhaul of the Inner Line Permit (ILP) system in Arunachal Pradesh marks a major shift in governance and internal security. It strengthens the historic protections under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873, while modernising enforcement for today’s challenges. For UPSC and APPSC aspirants, this topic is crucial because it connects tribal rights, federalism, migration, security, and digital governance.
Sources:
- https://assamtribune.com/north-east/arunachal-to-launch-fully-digital-ilp-system-5000-violators-detected-this-year-1598782
- https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/arunachal-pradesh/arunachal-cm-pema-khandu-announces-major-digital-overhaul-of-ilp-to-strengthen-monitoring/article70310726.ece
- https://www.sentinelassam.com/topheadlines/arunachal-pradesh-set-to-introduce-digitised-ilp-system-says-cm-pema-khandu
- https://www.eilp.arunachal.gov.in/actDetails
The Inner Line Permit (ILP) is an official travel document mandated under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation (BEFR), 1873. It is required by all non-residents of Arunachal Pradesh, including Indian citizens, to enter the State. The ILP protects tribal land rights, safeguards indigenous identity, and regulates movement in sensitive border regions.
The fully digitised ILP system enables real-time visitor tracking, automated verification, detection of overstaying, and seamless backend integration with enforcement agencies. This digital upgrade enhances transparency, reduces manual errors, and strengthens internal security along the India–China border.
Yes. Arunachal Pradesh has introduced online and e-ILP facilities for domestic travellers, making the application and approval process faster and more convenient. Foreign tourists (except Bhutanese citizens) must apply for a Protected Area Permit (PAP) instead of an ILP.
Key challenges include balancing development with protective regulations, restricted tourism inflow, limited inter-state labour movement, digital access barriers in remote districts, and continued illegal migration through porous borders despite ILP enforcement.
The ILP framework protects the cultural, social, and customary rights of indigenous tribes and prevents illegal settlement. For national security, it acts as a frontline regulation tool, especially in Arunachal Pradesh’s sensitive border areas with China, helping monitor labour movement, prevent infiltration, and support strategic oversight.












