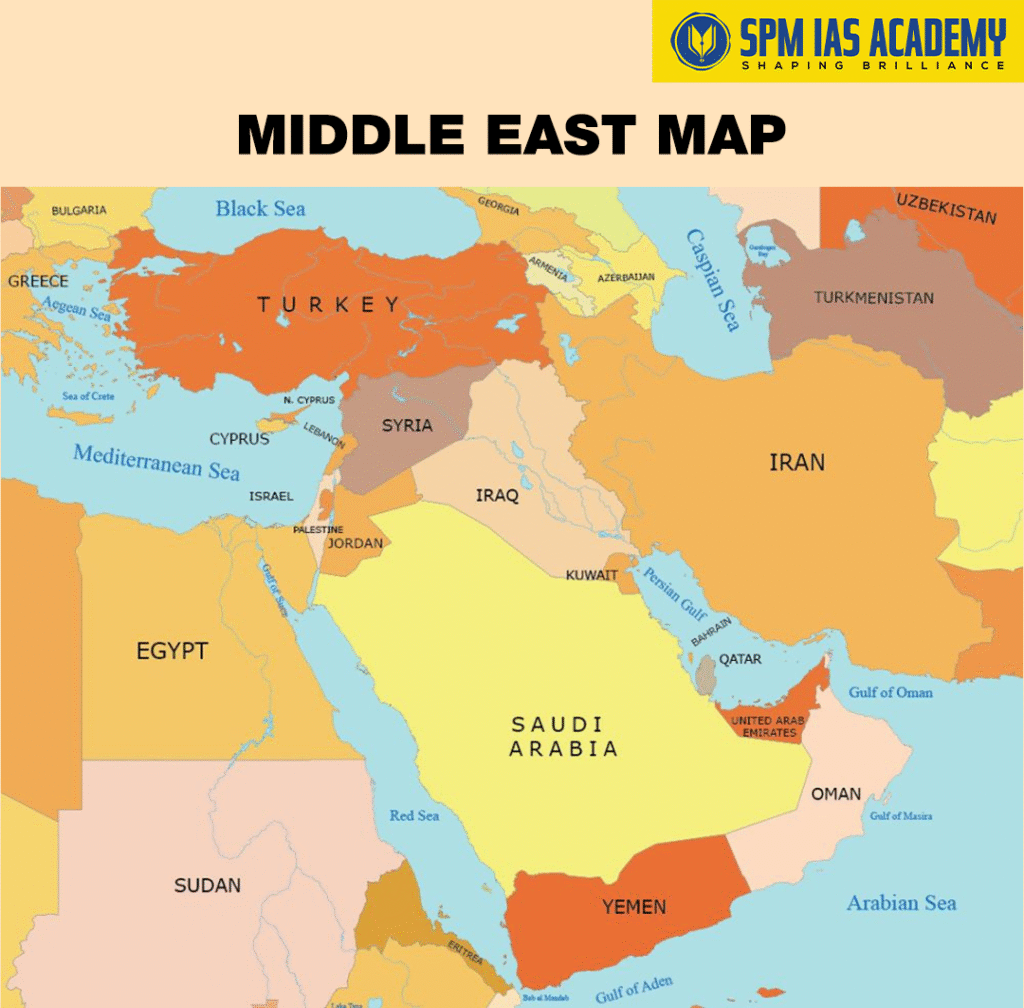
The Middle East Countries form one of the most geopolitically and economically significant regions in the world. The area spans Western Asia and parts of Northern Africa, serving as a bridge between Asia, Africa, and Europe. Moreover , it is famous for its ancient civilizations, cultural richness, and abundant natural resources, particularly oil and gas. Over the years, the Middle East has played a vital role in shaping global trade routes, diplomacy, and energy security.
Hence , understanding the Middle East Countries is essential because it directly impacts India’s foreign policy, strategic interests, and economic ties with the region.
Middle East Countries List and Their Capitals
The List of Middle East Countries includes around 25 nations, each with its own cultural identity and political significance. Capitals in the Middle East are not only administrative centers but also the hubs of trade, religion, and governance.

Below is the complete list of Middle East Countries and their capitals:
| Country | Capital |
| United Arab Emirates,Algeria,Jordan,Turkey,Greece,Iraq,Azerbaijan,Lebanon,Egypt,Syria,Qatar,Pakistan,Afghanistan,Sudan,Kuwait,Bahrain,Oman,Cyprus,Saudi Arabia,Morocco,Yemen,Georgia,Iran,Libya,and Tunisia. | Abu Dhabi,Algiers,Amman,Ankara,Athens,Baghdad,Baku,Beirut,Cairo,Damascus,Doha,Islamabad,Kabul,Khartoum,Kuwait City,Manama,Muscat,Nicosia,Riyadh,Rabat,Sanaa,Tbilisi,Tehran,Tripoli,Tunis. |
Geopolitical and Economic Importance of Middle East Countries
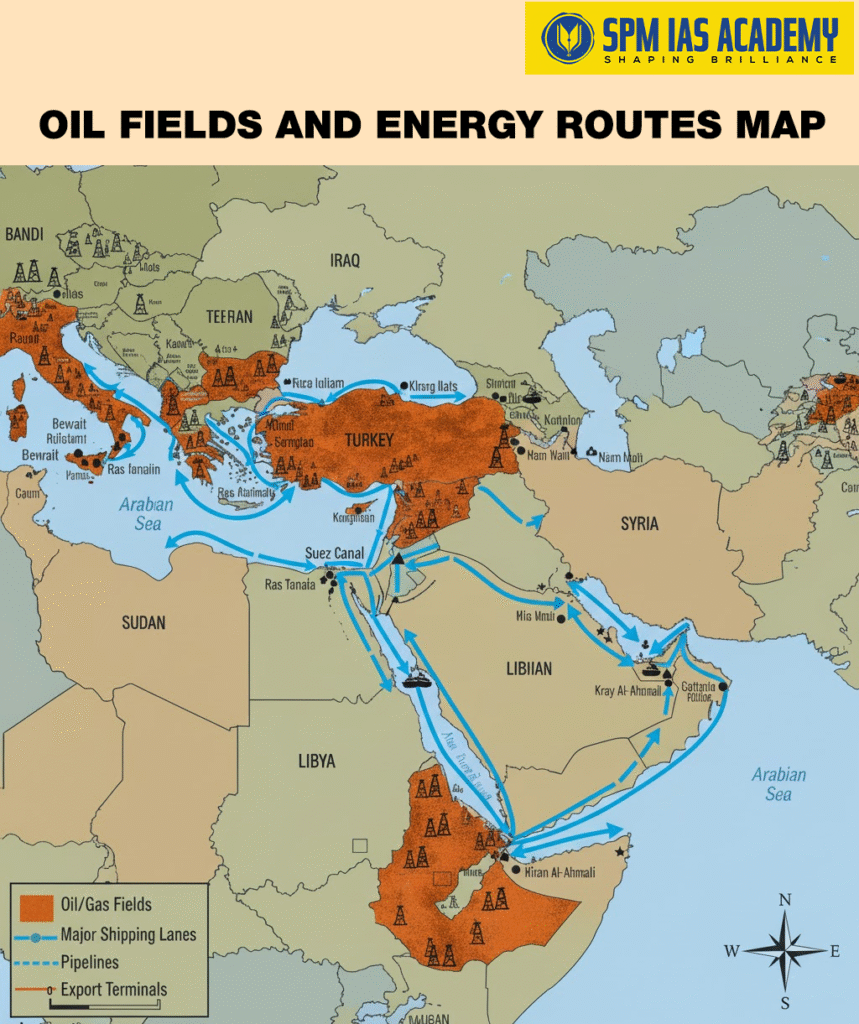
The Middle East Countries play a central role in world politics and global economics. Hence , this importance comes from their strategic location, natural resources, and religious influence.
Here’s why the region holds such importance:
- Strategic Location: The Middle East lies between Asia, Africa, and Europe, covering vital maritime choke points like the Suez Canal, Strait of Hormuz, and Bab-el-Mandeb.
- Energy Powerhouse: Second , nearly 48% of global oil reserves are located in Middle Eastern nations, making the region a backbone of the world’s energy supply.
- Religious Significance: Holy cities like Mecca, Medina, Jerusalem, and Bethlehem make the region spiritually vital for billions across the world.
- Trade and Connectivity: Fourth , the region acts as a major hub for global shipping and air routes, linking East and West economically and strategically.
Middle East Countries Map
The Middle East Countries Map includes:
- Firstly , Eastern Mediterranean nations such as Syria, Lebanon, and Israel
- Second, the Arabian Peninsula countries including Oman, UAE, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia
- Lastly , Gulf States such as Qatar, Bahrain, and Kuwait
Additionally, the Red Sea, Persian Gulf, and Strait of Hormuz are key maritime routes that make the Middle East a cornerstone of international trade and energy transportation.
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE EC)
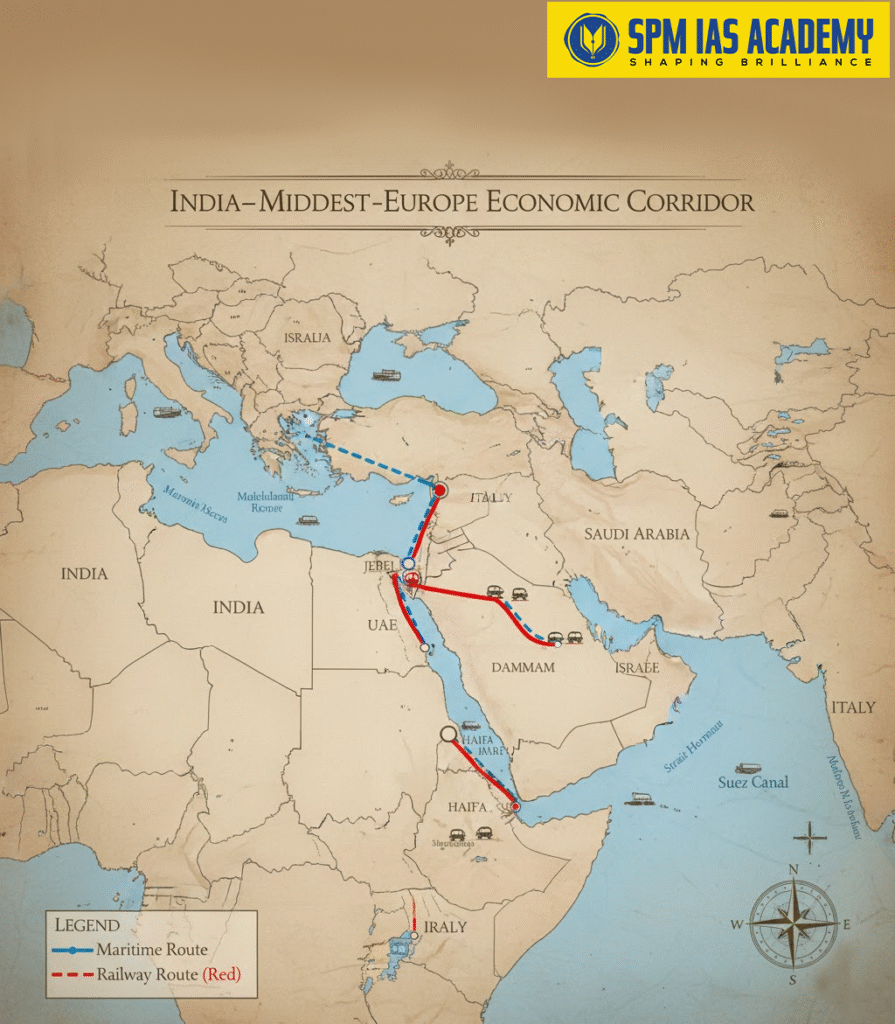
The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEE EC) is a transformative initiative designed to strengthen trade, connectivity, and cooperation among India, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Components of the IMEE EC
- Railway Infrastructure: A modern rail network connecting India to the Arabian Gulf and Europe, ensuring faster and cheaper trade.
- Digital Connectivity: High-speed internet cables to enhance digital infrastructure and secure communication lines.
- Energy Infrastructure: Clean energy projects, especially green hydrogen pipelines, promote sustainability.
- Sustainability Measures: Focused efforts to build eco-friendly logistics and renewable energy systems.
Benefits of the IMEE EC
- Enhanced Global Supply Chain: Firstly , it strengthens India’s trade connectivity with Europe and West Asia while reducing dependency on traditional sea routes.
- Strategic Advantage: Secondly , it improves India’s role in global geopolitics, balancing China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- Economic Growth: It boosts industries like logistics, infrastructure, and renewable energy, generating employment.
- Food Security: Moreover , it creates a reliable system for the transport of essential goods and agricultural produce across continents.
- Sustainability: Lastly , it promotes the use of clean energy and reduces carbon emissions globally.
Conclusion

The Middle East Countries represent a unique blend of culture, commerce, and global influence. Their strategic location, vast energy reserves, and religious importance make the region one of the most vital areas for world affairs. For India, strong relations with Middle Eastern nations are crucial for ensuring energy security, diversifying trade, and fostering diplomatic cooperation.
Understanding the Middle East Countries will help you and policymakers to grasp global power dynamics and India’s foreign policy priorities. As the world continues to evolve, the Middle East remains a crucial link between the past, present, and future of international relations.
FAQs
No, Indians are not considered Middle Eastern. India is located in South Asia, geographically distinct from the Middle East region.
The international definition often includes countries from Western Asia and Northern Africa, whereas the traditional Middle East list focuses on Arabian Peninsula nations and surrounding states.
The Middle East includes around 25 countries, such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Egypt, and the UAE, among others.
No, India is not a Middle Eastern country. It shares close cultural and economic ties with the Middle East but is geographically part of South Asia.
People from countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, and Egypt are generally classified as Middle Eastern based on their geographic and cultural roots.












