Why is the news?
Parliament passed the Promotion and Regulation of Online Gaming Act, 2025. The bill aims to ban Real Money Games (RMGs). It also promotes e-sports and social gaming. Furthermore, it creates India’s first national framework. This framework resolves fragmented state-level gaming laws.
Introduction
The Indian Parliament has passed the Online Gaming Act 2025. This marks an important step in regulating the rapidly growing digital gaming industry. The Act aims to strike a balance between promoting innovation in e-sports and social gaming. At the same time, it addresses the social and economic harms caused by Real Money Games (RMGs).
Government data estimates that Indians lose about Rs. 15,000 crore annually on such games. This ban on real money games comes in response to growing worries about addiction, suicides, fraud, and tax evasion connected to online gambling.
In this article, we will look into the Online Gaming Act 2025 and why it is important to understand.
What are the Key Features of the Online Gaming Act 2025?
Below are the key features of the Online Gaming Act 2025.
1. The Online Gaming Act 2025 classifies online games into three categories:
- E-sports: The National Sports Governance Act, 2025, officially recognizes certain online games as esports. These include competitive video games. They feature performance-based prize pools. Some examples of these games are “Call of Duty” and “Grand Theft Auto”.
- Social Gaming: Social games are games played primarily for recreation or educational purposes. These games often do not have any monetary stakes. The Act encourages their development through budgetary support.
- Real Money Games (RMGs): Online games that involve monetary stakes fall under the RMGs. These games are usually played with money, credits, or convertible tokens. Some examples of these games include Poker, Rummy, Fantasy Cricket, and Ludo variants. Thus, this bill states a ban on Real Money Games.
2. The ban on Real Money Games also extends to advertisements and celebrity endorsements. It also includes platforms offering real money games (RMGs). Several high-profile celebrities had previously endorsed such platforms. Thus, this raises concerns about their influence on youth.
What are the Penalties and Enforcement Mechanisms of the Online Gaming Act 2025?
There are severe penalties for promoting RMGs. These penalties and enforcement are mentioned in the Online Gaming Act 2025. The Act imposes penalties to curb illegal activities. These are important for understanding India’s Online Gaming Bill 2025.
1. Offering or facilitating RMGs: Up to three years of imprisonment. They may also incur fines of up to ₹1 crore.
2. Unlawful advertisements: Celebrity endorsers and influencers promoting such platforms risk two years of imprisonment. Additionally, they can face penalties of up to ₹50 lakh.
3. Unlawful transactions: Financial institutions facilitating transactions for these platforms may face similar consequences.
Under the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023, offences are classified as cognisable and non-bailable. To ensure enforcement, the government has given authority to CERT-IN (Indian Computer Emergency Response Team). They can block or disable apps that do not comply with the regulations. Additionally, the government may collaborate with Interpol to address offshore operators who are circumventing Indian laws. Notably, the Act does not criminalise players; instead, it focuses on targeting the operators and promoters involved.
What is the Government’s Rationale Behind the Online Gaming Act 2025?
The government’s justification for the ban on real money games centers on two concerns: national security and public health. Officials cite evidence linking these platforms to money laundering, terror financing, and tax evasion. The IT Ministry has highlighted cases where gaming platforms served as communication channels for terrorist organizations. These platforms also facilitated fund transfers.
The government has emphasized that this initiative is not a hasty response. It is a considered action. This decision comes in light of concerning trends. From a public health perspective, the government points to statistics.
1. Addiction: Tamil Nadu reported 47 suicides linked to online gaming addiction between 2019 and 2024.
2. Suicides: WHO has linked RMGs to compulsive behaviour. Karnataka alone reported 32 gaming-related suicides in 31 months.
3. Financial fraud: A Defence Ministry report revealed that the Chinese app FIEWIN defrauded Indians of Rs. 400 crore.
4. Tax evasion: Reports indicate that gaming firms evaded over Rs. 30,000 crore in GST liabilities. Additionally, they avoided Rs. 2,000 crore in income tax.
5. Money laundering and terrorism funding: A 2023 Parliamentary Panel flagged gaming portals as potential conduits for terror financing.
These platforms use manipulative design features. They also employ addictive algorithms that drive compulsive behavior. This behavior can lead to impulsive spending. Impulsive spending can create financial hurdles for families. Union Minister Vaishnaw emphasized that certain platforms have been linked to illegal activities. These activities include:
- money laundering,
- financial fraud,
- financing of terrorism.
Such issues affect the security and sovereignty of the state.
What are the Legal and Constitutional Challenges of the Online Gaming Act 2025?
Below are the legal difficulties faced by the Online Gaming Act 2025:
1. Skill vs. Chance Debate: The law does not differentiate between games of skill and games of chance. Games of skill include activities such as fantasy sports or Rummy. Critics argue that this lack of distinction violates Article 19(1)(g). Article 19(1) guarantees the right to trade and occupation.
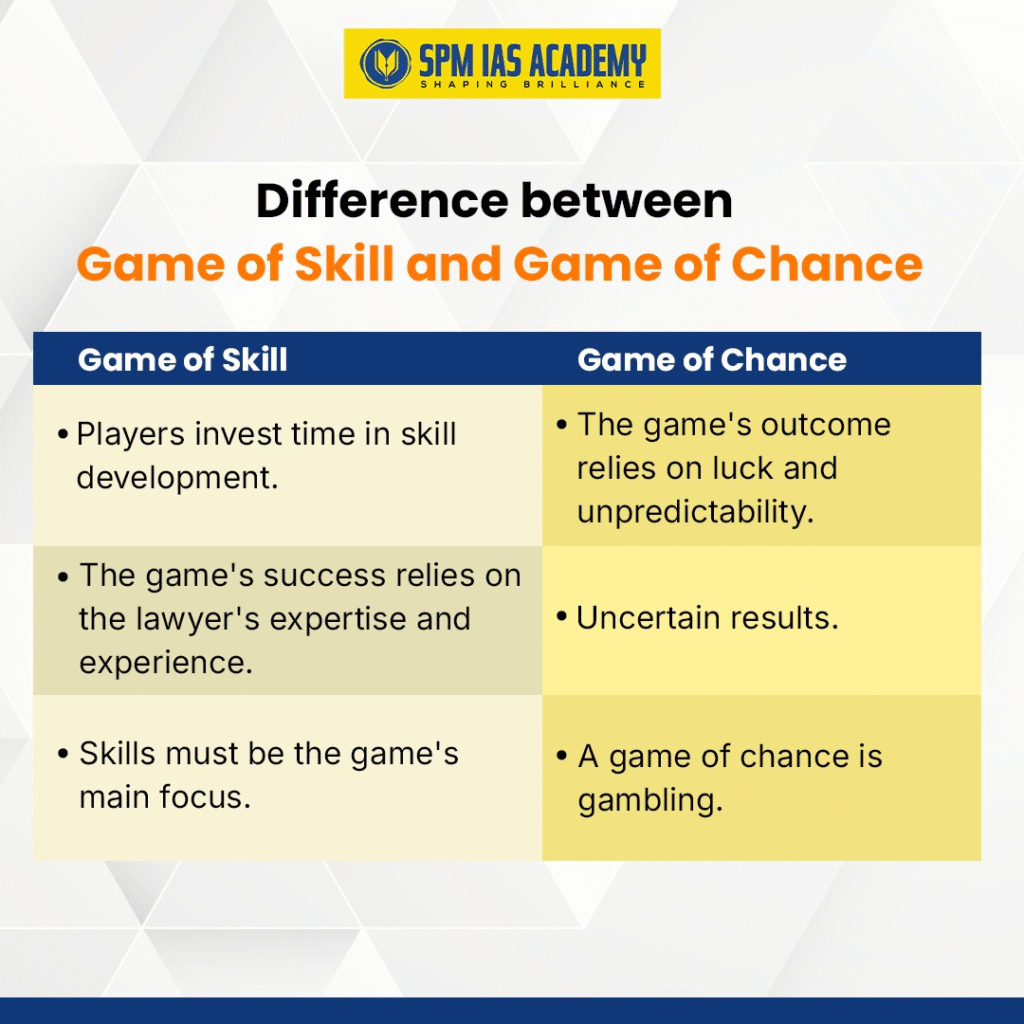
2. Jurisdictional Overlap: Betting and gambling fall under State jurisdiction. This is outlined in Entries 34 and 62 of the State List. States like Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu have already banned online gambling. This has created legal ambiguities.
3. Supreme Court Intervention: Earlier rulings held Rummy and Fantasy Sports as games of skill. The SC has also stayed retrospective GST notices to gaming firms. Future judgments will determine how far the Act aligns with constitutional guarantees.
Online Gaming Act 2025: Promoting E-sports and Social Gaming
1. Unlike the ban on Real Money Games, the Act actively promotes safe online gaming ecosystems:
- Government funding from the Consolidated Fund of India will support e-sports and social gaming.
- Provisions encourage educational and recreational games, fostering innovation and digital inclusion.
- No restrictions have been placed on minors accessing social games or e-sports, though critics argue that stronger safeguards are needed.
2. This dual approach shows India’s ambition to become a hub for online gaming. At the same time, it aims to protect citizens from exploitative practices.
Conclusion
The ban on real money games and the Online Gaming Act 2025 represent more than just regulatory policy. It reflects India’s approach to governing its digital economy. While protecting citizens from harm is important, prohibiting an industry may create more problems than it solves.
As the legislation moves through the parliamentary process, it faces legal challenges. Stakeholders must engage in dialogue to find a solution. A regulatory framework that addresses concerns about addiction and fraud could better serve India’s interests. It should preserve innovation and promote economic growth instead of relying on prohibition.
The success or failure of this policy will influence how India regulates other digital sectors. For a nation aspiring to become a technology leader, India’s approach to penalties in the gaming industry will be closely monitored.
Frequently Asked Questions
It bans all Real Money Games (RMGs) and their advertisements in India.
All real money games involve monetary deposits or fees.
The Central government will establish a regulatory authority in collaboration with CERT-IN, enforcing compliance.
Up to 3 years imprisonment and ₹1 crore fine.
It promotes e-sports as recognised competitive games and encourages social gaming for recreation and education.
Up to 2 years imprisonment and ₹50 lakh penalty.
National security and public welfare concerns.
Critics argue it erases the distinction between games of skill and chance, raising constitutional concerns and industry challenges.












