Why was Kameng river in the News?
Recently, reports highlighted that the Kameng River has significant potential to develop as a fishing tourism destination in Arunachal Pradesh. With its pristine Himalayan ecology and rich aquatic biodiversity, the river is increasingly being viewed as a viable avenue for eco-tourism, livelihood generation, and sustainable development in the state.
What Is the Kameng River? Key Facts, Origin, and Geographical Importance:
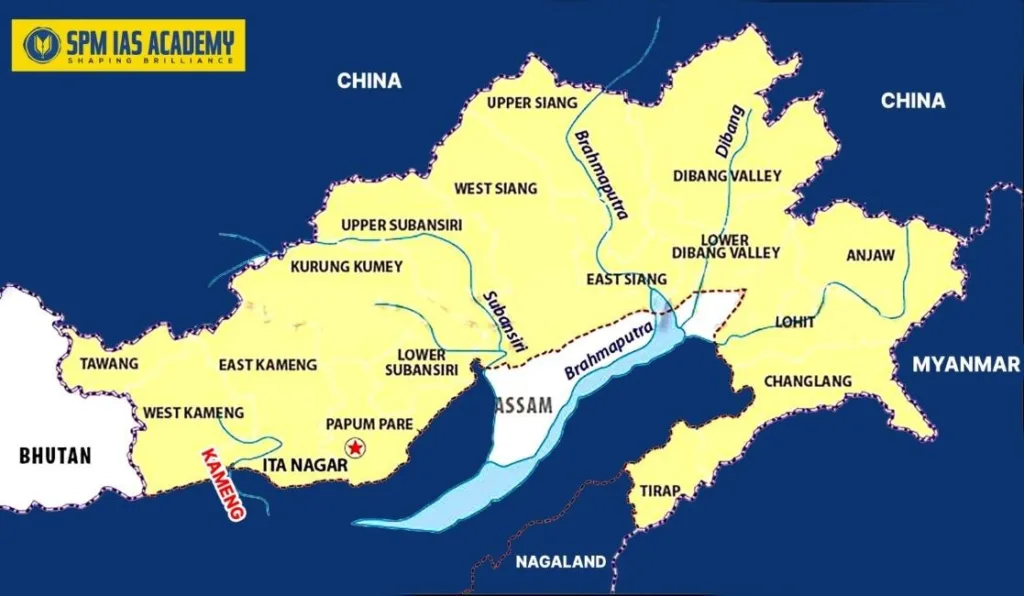
- To begin with, the Kameng River is a major Himalayan River of Arunachal Pradesh, flowing for about 264 km.
- It was previously known as Bharali river and now it is known as Jia-Bharali in Assam.
- It originates from a glacial lake below the snow-capped Gori Chen Mountain at an elevation of 6,300 metres in Arunachal Pradesh. It joins the Brahmaputra River at Tezpur in Assam.
- Importantly, the river flows through East Kameng district and West Kameng district forming a boundary between these two districts. This region is known for rich biodiversity and tribal cultural heritage.
- Historically, during the medieval period (13th to early 16th century), the Kameng river formed the boundary between the Chutiya kingdom and the Kamata kingdom.
- The Kameng river forms the boundary between the Sessa Orchid Sanctuary and Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary to its west and the Pakke Tiger Reserve to the east.
- Some of its important tributaries are Tippi, Tenga, Bichom and Dirang Chu.
- Owing to its clean waters, fast currents, and diverse fish species, the Kameng River is particularly suitable for catch-and-release fishing tourism.
What is Fishing Tourism?
Fishing tourism refers to recreational travel centred around fishing activities, where tourists visit natural water bodies primarily for sport, leisure, or experiential fishing.
- Unlike commercial fishing, fishing tourism emphasises conservation, recreation, and sustainability.
- In many models, catch-and-release is followed to protect fish populations and aquatic ecosystems.
- Globally, fishing tourism is considered a form of nature-based and eco-tourism. It contributes to local economies without ecological degradation.
What are the types of Fishing Tourism?
There are various types of fishing tourism. Some of the important types of fishing tourism are as given below:
- Recreational Fishing Tourism: Leisure-based fishing for tourists.
- Sport Fishing Tourism: Competitive or challenge-based fishing experiences.
- Fly-Fishing Tourism: A niche, high-end segment popular among international tourists.
- Catch-and-Release Fishing: Promotes conservation while ensuring tourist engagement.
What is the potential of Arunachal Pradesh for Fishing Tourism?
Arunachal Pradesh possesses unique natural advantages that make it suitable for fishing tourism:
- Firstly, the state has numerous perennial rivers such as Subansiri, Kameng, Dibang etc. originating in the Himalayas. These rivers offer ideal habitats for indigenous fish species.
- Secondly, the region remains ecologically less disturbed, ensuring clean and oxygen-rich waters.
- Thirdly, the presence of tribal communities with traditional ecological knowledge adds cultural value to tourism experiences.
- Lastly, low population density and scenic landscapes make the state attractive for high-value, low-impact tourism.
What are the opportunities of Kameng River Fishing Tourism?
The development of fishing tourism along the Kameng River presents multiple opportunities:
- Economic and Livelihood Opportunities:
- Creation of alternative livelihoods for local youth through guiding, hospitality, and eco-services.
- Boost to homestays, local transport, handicrafts, and food services.
- Encouragement of community-based tourism models, ensuring inclusive growth.
- Environmental and Conservation Benefits:
- Fishing tourism, when regulated, incentivises river conservation and biodiversity protection.
- Catch-and-release practices help maintain fish population balance.
- Increased awareness about freshwater ecosystems and climate sensitivity of Himalayan rivers.
- Governance and Policy Dimensions:
- Provides scope for state-level eco-tourism policies and public-private partnerships.
- Requires formulation of clear guidelines on fishing permits, seasons, and conservation norms.
- Can align with broader objectives of sustainable tourism and green economy.
What are the Challenges and Concerns of fishing tourism in the Kameng river?
- One of the important concerns is the risk of over-tourism and ecological stress if unregulated.
- Another concern is the need for capacity building of local communities in relation to fishing tourism. So that they can get economic and social benefits.
- Moreover, the infrastructure gap in remote riverine areas is another challenge. Here, developing infrastructure with environmental protection is another challenge.
What are the Way Forward for the above challenges and concerns?
- Firstly, develop a state fishing tourism policy with strict ecological safeguards.
- Then, promote catch-and-release-only zones in ecologically sensitive stretches.
- Another important way forward could be to involve local tribal communities as stakeholders and beneficiaries.
- Lastly, integrate fishing tourism with eco-tourism, adventure tourism, and cultural tourism.
Conclusion:
The Kameng River represents a promising convergence of ecology, economy, and tourism in Arunachal Pradesh. If developed responsibly, fishing tourism can emerge as a sustainable growth engine, supporting livelihoods while preserving the fragile Himalayan ecosystem.
Prelims Practice MCQ:
Q. With reference to the Kameng River, consider the following statements:
- It originates from a glacial lake below the snow-capped Gori Chen Mountain in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is known as the Bharali River in Assam and joins the Brahmaputra at Tezpur.
- It forms the boundary between the Pakke Tiger Reserve to the west and the Eaglenest Wildlife Sanctuary to the east.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct Answer: (a)
Mains Practice Question:
Discuss the potential of the Kameng River as an emerging fishing tourism destination in Arunachal Pradesh. How can fishing tourism contribute to sustainable livelihoods while ensuring ecological conservation in Himalayan River systems?
Source: Arunachal Times
FAQ:
Fishing tourism refers to recreational travel focused on fishing activities. Here tourists visit natural water bodies for leisure, sport, or experiential fishing. It often follows catch-and-release practices to promote conservation and sustainable use of aquatic ecosystems.
The Kameng River has clean, fast-flowing Himalayan waters, rich fish diversity, and relatively undisturbed ecology, making it ideal for catch-and-release, fly-fishing, and recreational fishing tourism.












