The biosphere is the global ecological system integrating all living beings and their relationships, including their interaction with the elements of the lithosphere (land), hydrosphere (water), and atmosphere (air). It encompasses all ecosystems on Earth, where life exists, ranging from the deepest oceanic trenches to the upper reaches of the atmosphere.
Extent of the Biosphere: The biosphere extends from the deepest layers of the Earth’s crust, where microbial life thrives, to the upper atmosphere, where life can survive in limited forms. This zone, known as the “zone of life,” includes:
- Lithosphere: The Earth’s crust and upper mantle, where terrestrial life exists.
- Hydrosphere: All water bodies, including oceans, rivers, lakes, and groundwater are home to aquatic organisms.
- Atmosphere: The gaseous layer surrounding Earth, which supports airborne life and influences climate.
The biosphere is not uniformly distributed; it is thickest at the Earth’s surface, particularly where conditions like temperature, moisture, and sunlight are optimal for life. However, life has adapted to extreme conditions, allowing the biosphere to extend into the harshest environments, such as deep-sea hydrothermal vents and high-altitude regions.
Importance of the Biosphere:
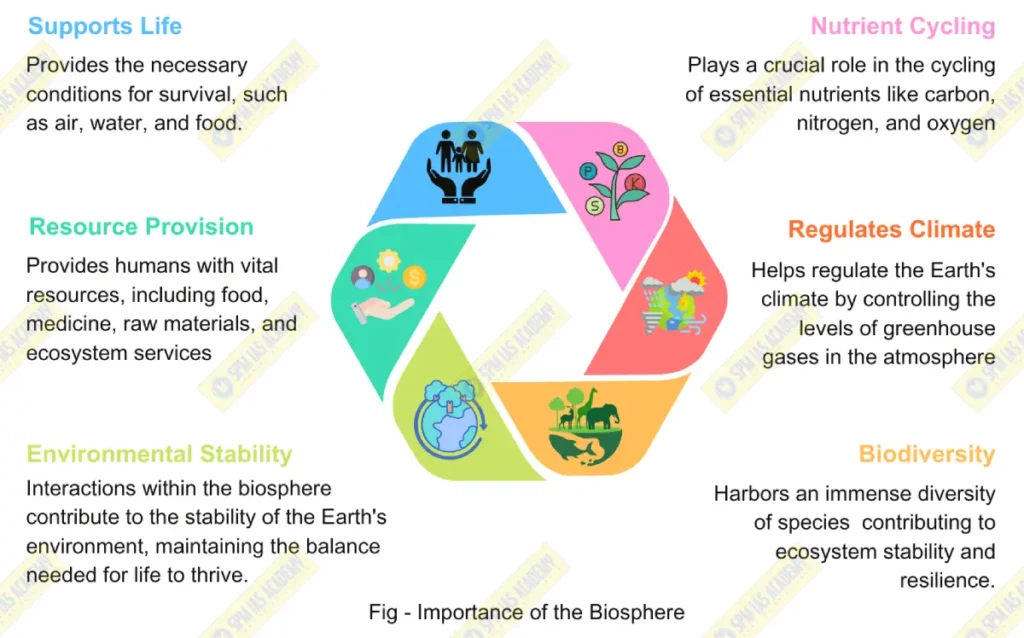
- Supports Life: The biosphere is the primary habitat for all living organisms, providing the necessary conditions for survival, such as air, water, and food.
- Nutrient Cycling: The biosphere plays a crucial role in the cycling of essential nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. These cycles maintain the balance of ecosystems and ensure the availability of nutrients for all forms of life.
- Regulates Climate: Through processes like photosynthesis and respiration, the biosphere helps regulate the Earth’s climate by controlling the levels of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, in the atmosphere.
- Biodiversity: The biosphere harbors an immense diversity of species, each contributing to ecosystem stability and resilience. Biodiversity ensures that ecosystems can adapt to changes and continue to function effectively.
- Resource Provision: The biosphere provides humans with vital resources, including food, medicine, raw materials, and ecosystem services like pollination, water purification, and soil fertility.
- Environmental Stability: The interactions within the biosphere contribute to the stability of the Earth’s environment, maintaining the balance needed for life to thrive. It acts as a buffer against environmental changes, helping to mitigate the effects of natural and human-induced disturbances.
In summary, the biosphere forms the essential foundation for life on Earth, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecosystems and supporting biodiversity. Its health and stability are critical for achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly SDG 13 (Climate Action), SDG 14 (Life Below Water), and SDG 15 (Life on Land). Preserving and protecting the biosphere is vital for ensuring the long-term sustainability of Earth’s environment and the well-being of all species, including humans.
Check out UPSC Coaching Centre Guwahati | APSC Coaching Centre Guwahati | Crack APSC Exam | UPSC Civil Services Exam | Ethics Paper in UPSC Exams












