Biodiversity, encompassing the variety of all life forms on Earth, is a cornerstone of ecological stability and human survival. Beyond its environmental significance, biodiversity directly supports economies by providing resources, ecosystem services, and opportunities for innovation and livelihood generation. In a localized context, the sustainable management of biodiversity can catalyze economic development while ensuring ecological resilience.
Economic Benefits of Biodiversity
1. Resource Provisioning: Supplies essential resources like food, fuel, timber, and medicines, critical for industries like agriculture, forestry, and healthcare.
○ Example: India’s pharmaceutical industry utilizes plants such as neem and turmeric for medicines.
2. Ecosystem Services: Provides services like pollination, water purification, and climate regulation, vital for agriculture and human well-being.
○ Example: Mangrove forests in India protect coastal infrastructure and communities while supporting fisheries.
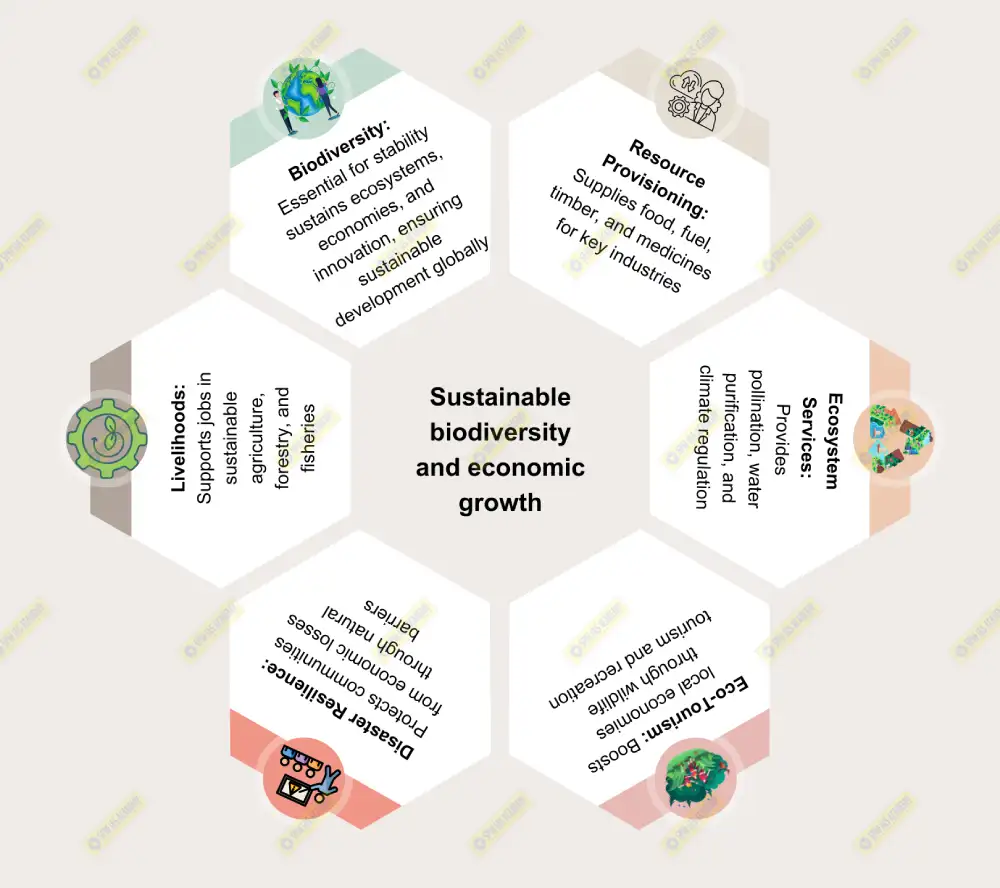
3. Tourism and Recreation: Biodiversity-rich landscapes attract eco-tourism, creating employment and boosting local economies.
○ Example: Jim Corbett National Park generates significant revenue through wildlife tourism.
4. Cultural and Traditional Values: Many communities derive their livelihoods from biodiversity-linked traditional crafts, foods, and rituals, which have economic value.
○ Example: Handicrafts made from bamboo and jute in rural India.
5. Scientific Research and Innovation: Offers the raw material for developing new products, technologies, and pharmaceuticals.
○ Example: Innovations in bio-pesticides and organic farming derived from biodiversity research.
How Biodiversity Conservation Promotes Economic Activities
- Sustainable Agriculture: Conserving biodiversity ensures the availability of resilient crop varieties and promotes organic farming.
○ Example: Seed banks in India protect indigenous crop varieties, enhancing farmers’ income. - Eco-Tourism and Hospitality: Protected biodiversity areas foster tourism, generating income for local communities through hospitality services and guiding.
○ Example: The Sundarbans’ tiger reserves boost eco-tourism in West Bengal. - Livelihood Opportunities: Conservation projects create employment in areas like sustainable forestry, fisheries, and agro-based industries.
○ Example: Honey collection from forested regions of Uttarakhand and Tamil Nadu. - Carbon Credits and Global Funding: Conserved biodiversity helps mitigate climate change, attracting funds through carbon credit schemes and international conservation grants.
○ Example: REDD+ programs in India incentivize forest conservation. - Value Addition to Local Products: Promotes branding of unique biodiversity-linked products for premium pricing.
○ Example: GI-tagged products like Mysore Sandalwood or Darjeeling Tea benefit from biodiversity conservation. - Disaster Resilience: Preserved ecosystems like wetlands and mangroves act as natural barriers, reducing disaster-related economic losses.
○ Example: The Sundarbans mangroves protect against cyclones, saving lives and assets.
Biodiversity, when conserved and sustainably managed, offers multifaceted economic benefits, from securing livelihoods to attracting investments and promoting eco-tourism. In an era of climate change and resource depletion, biodiversity conservation is not merely an environmental imperative but a key strategy for fostering sustainable and inclusive economic growth. By aligning local development with conservation efforts, communities can build resilient economies that thrive in harmony with nature.











