General Studies Paper 1 (GS-1) is a crucial part of the UPSC Civil Services Mains Examination (CSE). It focuses on assessing a candidate’s understanding of Indian heritage, history, geography, and society. The topics covered in this paper are vast and multidimensional, requiring both factual knowledge and analytical depth.
Below is the UPSC Mains GS Paper 1 syllabus as officially prescribed by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
(Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World and Society)
- Indian Culture – Salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
- Modern Indian History from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present- significant events, personalities, issues.
- The Freedom Struggle — its various stages and important contributors/contributions from different parts of the country.
- Post-independence Consolidation and Reorganization within the country.
- History of the World will include events from the 18th century such as Industrial Revolution, world wars, Redrawal of National Boundaries, Colonization, Decolonization, political philosophies like Communism, Capitalism, Socialism etc.— their forms and effect on the society.
- Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
- Role of Women and Women’s Organization, Population and Associated Issues, Poverty and Developmental issues, Urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
- Effects of Globalization on Indian society.
- Social Empowerment, Communalism, Regionalism & Secularism.
- Salient features of World’s Physical Geography.
- Distribution of Key Natural Resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India).
- Important Geophysical Phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclones etc., geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
IAS Mains General Studies – I
The table below mentions the subjects included in UPSC Mains Paper-II which is also called the Mains GS 1 along with NCERT Notes on each subject:
| Topics | Sub-topics |
|---|---|
| Indian Heritage and Culture | Art and culture |
| History | Ancient History |
| Medieval History | |
| Modern History | |
| Post-Independence India | |
| World History | |
| Geography of the World | World and Indian Geography |
| Society | Indian Society |
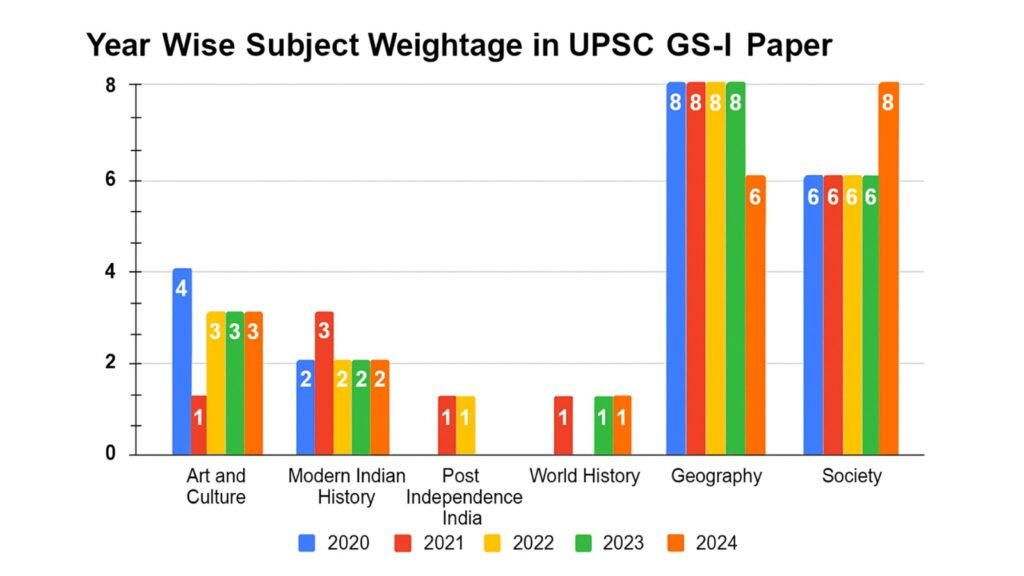
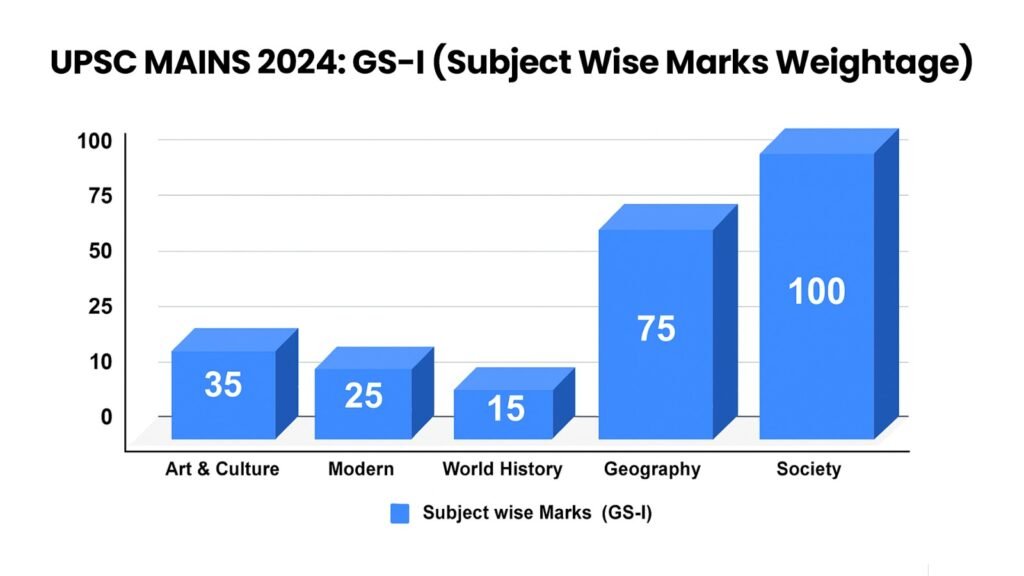
Focus Areas in Mains General Studies-I
Below are the key focus areas in Mains General Studies Paper-I that every aspirant should concentrate on during their preparation:
| Art and culture | |
|---|---|
| Indian Culture – Salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times | |
| Indian Art Forms | • Indian Paintings • Mural Paintings • Miniature Paintings • Mughal, Rajput, Pahari Paintings • Dances in India • Classical Dance Forms • Folk Dance Forms • Modern Dance • Music • Classical Music • Folk Music • Puppetry • String Puppets • Shadow Puppets • Rod Puppets • Glove puppets • Modern Puppetry • Tribal Puppetry • Pottery • Ochre Coloured Pottery(OCP) • Black and Red Ware (BRW) • Painted Grey Ware (PGW) • Northern Black Polished Ware (NBPW) • Glazed and Unglazed PotteryDrama/Theatre • Classical Sanskrit Theatre • Regional Theatre • Modern Theatre • Martial Arts • Thang • TaGatka • Kalaripayattu • Mallakhamb • Silambam • Other Important Martial Arts • Visual Art • Sculptures of Harappan Civilization • Sculptures of the Mauryan Age • Post-Mauryan Period • Jain Sculptures • Buddhist Sculpture • Gupta Sculpture • Medieval School of Sculpture • Modern Indian Sculpture • Bhakti & Sufi Movements • Spread of Bhakti and Sufi Movements • Women Poets of Bhakti |
| Literature | • Classical Sanskrit Literature • Vedas, Upanishads, Puranas • Books written by Kalidasa, Vishakhadatta etc • Ancient Buddhist • Literature • Ancient Jainism Literature • Early Dravidian Literature (eg Sangam Period) • Medieval Literature • Trends in Medieval Literature • Modern Indian Literature |
| Architecture | • Harappan Architecture • Mauryan Architecture • Post-Mauryan Period Gupta PeriodTemple Architecture • Nagara StyleDravida Style • Vesara StyleCave Architecture • Buddhist CaveJaina CavesGupta Period CavesMedieval and Indo-Islamic Architecture • Imperial Style Delhi Sultanate • Provincial Style • Mughal Style • Sikh Style of Architecture • Rajput Architecture • Salient features • Colonial Architecture & Modern Architecture • European Influence • Indo-Saracenic Architecture • Post-Independence Period • Contribution of Buddhism & Jainism to the Development of Indian Architecture • Rock Cut Architecture • South Indian • Western Indian • Eastern Indian |
| Ancient History | |
|---|---|
| Pre-historic | Stone Age Chalcolithic Age Iron Age |
| Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) | • Town Planning • Harappan Society • Characteristics of Major Centers • Harappan Art & Architecture • Decline of Harappan Culture |
| Vedic Society | Original Home of Aryans • Socio- Economic Characters of Vedic • Society • Vedic Literature • Social Organization and Varna System • Religion and Thought |
| Pre-Mauryan Period | Mahajanapadas Haryanka dynasty Shishunaga dynasty Nanda dynasty |
| Jainism and Buddhism | Gautam Buddha Mahavira Growth of Jainism and Buddhism |
| Mauryan Empire | Chandragupta and Bindusara Arthasastra (Book by Kautilya) Megasthenes Asoka and His Successors Asoka’s Inscriptions and Sites Asoka’ a Dhamma Mauryan. Administration, Economy, Society and Art Decline of Maurya |
| Post-Mauryan India | Arrival of Indo-Greeks, Shakas, Parthians & Kushana Satavahanas and Other Indigenous Dynasties Schools of Art: Gandhara; Mathura; Amravati Imperial Guptas Political history of Guptas Gupta Administration Development of Art & Culture Age of Golden age Economic Conditions Urban centres in Gupta periodHarshavardana Sources for Harsha’s Period Early life of Harsha Harsha’s Administration Important Officials of the empire Economy under Harsha Huen Tsang Society Religion The Southern Dynasties Satavahanas (230 BC TO AD 225) Pallavas (AD 330–796) Chalukyas (AD 535–1190) Pandyas of Madurai (AD 590–1323) Chola Dynasty (AD 850–1310) Rashtrakutas (AD 753–973) |
| Medieval History | |
|---|---|
| Delhi Sultanate | Slave (Ghulam) or Mamluk Dynasty Khilji Dynasty Tughlaq dynasty Sayyid Dynasty Lodi dynasty |
| Struggle for Empire in North India (Afghans, Rajputs and Mughals) | |
| Mughals | Babur Humayun Akbar Jahangir Shah Jahan Aurangzeb Later Mughals Decline of Mughal Empire |
| Sur Dynasties | |
| Maratha Empire | |
| Deccan Sultanate | Ahmednagar Sultanate Bijapur Sultanate Berar Sultanate Golconda Sultanate Bidar Sultanate |
| Modern History | |
|---|---|
| Modern Indian History from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present- significant events, personalities, issues The Freedom Struggle — its various stages and important contributors/contributions from different parts of the country | |
| Important Modern History Events Before 1857 | • Later Mughals • Regional powers in 18th Century • Carnatic Wars • Battle of Plassey & Buxar • Anglo-Mysore War • Anglo Punjab War • Socio-economic Condition of People • European Penetration of India British • Conquest of India • British Policies & Their Impact – Economic, Administrative & Socio-cultural • Socio-cultural Reform Movements • Uprisings Against British Pre-1857 |
| Revolt of 1857 | • Causes, Leaders, and Nature of revolt of 1857 • Suppression of revolt of 1857 • Consequences of Revolt of 1857 • Act of Good Governance 1858 |
| Growth of Nationalism in India (1858-1905) | • Political, Economic & Administrative Unification of the Country • Role of Western Education • Role of Press Rediscovery of India’s Past • Early Political Movements • Formation of INC • Era of Moderates |
| Growth of Militant Nationalism & Revolutionary Activities (1905-1918) | • Swadeshi & Boycott Movement • Surat Split • International Influence • Morley – Minto Reforms • Growth of Communalism |
| Beginning of Mass Nationalism (1919-1939) | • Mahatma Gandhi – His Ideas & Leadership • Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms • Rowlatt Act, Satyagrah and Jallianwala Bagh Massacre • Non-cooperation & Khilafat Movement • Swarajists & No-Changers • Emergence of New Forces – Socialist Ideas, Youth & Trade Unionism • Revolutionary Activity • Simon Commission & Nehru Report • Civil Disobedience Movement • Round Table Conferences • Communal Award & Poona Pact • Participation in Elections to Central Legislature (1934) & Provincial Assemblies (1937) • Government of India Act, 1935 |
| Towards Freedom & Partition (1939-1947) | • National Movement During World War II • August Offer • Individual Satyagraha • Growth of Communalism • Peasant Movements • State People’s Struggle • Cripps Mission • Quit India Movement • Wavell Plan • INA & Subhash Chandra Bose • Cabinet Mission • Nationalist Upsurge • Post-World War II • Independence with Partition |
| Post-Independence India | |
|---|---|
| Nation Building | • Partition and Its Aftermath • Integration of Princely States • Linguistic Regionalism in India • Reorganisation of States • Issue of Official Language • Tribal Consolidation • Regional Aspirations |
| Foreign Policy | • Non-Aligned Movement •Panchsheel • Wars with Pakistan & China • Nuclear Policy |
| Economy | • Planned Development • Green Revolution, Operation Flood & Cooperatives • Agrarian & Land Reforms • Industrial Reforms • LPG Reforms |
| Polity | • Era of One-Party Dominance • Emergence of Opposition Parties • Emergency: Crisis of Democratic Order • Rise of Regional Parties • Coalition Era |
| Social | • Popular Movements • Communalism • Indian Women Since Independence • Issue of Women and Evolution of Women Movement • Naxalism |
| Post-Independence Policy of Science And Technology | • India’s Policy in the Field of the Science and Technology • Impact of Economic Reform on the Science and Technology in India |
| World History | |
|---|---|
| History of the World will include events from 18th century such as Industrial Revolution, world wars, Redrawal of National Boundaries, Colonization, Decolonization, political philosophies like Communism, Capitalism, Socialism etc.— their forms and effect on the society | |
| Beginning of the Modern World | • Renaissance • Discovery of Sea Routes • Reformation • Counter Reformation • Industrial Revolution • European Nations Settle North America • Rise of Slave Trade • American War of Independence • Foundation of American Colonies • The Independence of United States of AmericaThe American Revolutionary War • What was the impact of the American Revolution?US Civil War • Impact of Civil War on USA • Global Impact of US Civil War • Impact on India • French Revolution • CausesThe revolution in France • France under Napoleon • Impact of revolution • Significance of revolution • Nationalism in Europe • Rise of the nation- state system • Unification of Italy • Unification of Germany • Rise of Capitalism, Colonialism & Imperialism • Colonialism • The age of Imperialism (1870-1914) • Imperialism in Asia • Analysis of ColonialismWorld War I • Causes of the War • Scope & Course of the War • Russian Revolution • Major events in pre-revolution Russia • Causes • Course of revolution • Consequences • Aftermath of the war • Post-Lenin Russia • End of the War & Peace Treaties • Consequences of the War • League of Nations |
| World Between the Two Wars | • Europe After the War – Fascism & Nazism • The Great Depression • Emergence of Soviet Union • Nationalist Movements in Asia & Africa • US as a Strong Power |
| World War II | • Fascist Aggression & Response of Western Democracies • Outbreak of the War • Theatres of the War • US Entry into the War • Global Nature of the War • The Holocaust • Resistance Movements • After-effects of the War |
| Decolonialisation & Redrawal of National Boundaries | • Europe after World War II • Cold WarRise of Asia & Africa • Developments in West Asia & North Africa • Spread of Communism • Korean WarVietnam War • Cuban Crisis • Collapse of Soviet Union |
| Concept, Types & Social Impact of Political Philosophies | • Communism • Capitalism • Socialism |
| Indian Society | |
|---|---|
| Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India | Indian Society ● Features of Indian Society ● Diversity in India: ● Caste ● Linguistic ● Social and Religious ● Race ● Tribe and Ethnicity ● Culture ● Challenges Posed by Diversity ● Concept of Unity ● Pluralism in Indian Society ● Unity in Diversity ● Inequality and Exclusion ● Family System in India ● Examples Illustrating the Above Concepts |
| Role of Women and Women’s Organization | Women’s Organizations in Indian History ● Types of Women’s Organizations ● Level of Penetration (Urban vs Rural, Class/Caste Lines) ● 19th Century Social Reform Movements and Early Women’s Organisations ● Women’s Role in Agrarian Struggles and Revolts ● Participation in the Freedom Struggle ● Prominent Women’s Organizations (with Examples) ● All India Women’s Conference (AIWC) ● Self Employed Women’s Association (SEWA) ● Mahila Samakhya ● National Federation of Indian Women (NFIW) ● Others (grassroots and regional groups) ● Problems Faced by Women’s Organizations ● Lack of Funding ● Political Interference ● Social Resistance ● Limited Grassroots Reach ● Is a Larger Vocal Role Possible? ● Ways to Achieve This: ● Legal and Policy Support ● Awareness Campaigns ● Media and Digital Empowerment ● Capacity Building ● Role of SHGs (Self Help Groups) ● Role of Microfinance Institutions in Women’s Empowerment |
| Population and Associated Issues | Demography of India ● Basic Demography of India ● Population Trends in India and Their Implications ● Causes and Effects of Overpopulation ● Challenges of Population Explosion ● Changing Age Structure of Indian Population ● Demographic Dividend: Boon or Bane for India ● Population Aging in India ● India’s Population Policy & Initiatives |
| Poverty and Developmental Issues | Development and Poverty ● Concept of Development and Poverty ● Types of Poverty ● Absolute Poverty ● Relative Poverty ● Urban & Rural Poverty ● Chronic & Transient Poverty ● Measurement of Poverty – Poverty Line ● Causes of Poverty ● Poverty as a Social Problem ● Socio-economic Spread of Poverty ● Consequences of Poverty ● Inequality ● Continuation of the Vicious Cycle of Poverty ● Who is Worst Affected by Poverty? ● Women ● Children ● Marginalized Communities ● Rural Poor ● Urban Informal Sector Workers ● Problem of Rising Urban Poverty ● Poverty Alleviation Initiatives ● Government Schemes (e.g., MGNREGA, PMAY, NFSA) ● NGO and Civil Society Roles ● Policy Shifts: ● From “Trickle Down” Economics ● To Inclusive or Pro-poor Development ● Relation Between Poverty Reduction and Development ● Poverty-Inequality-Development Nexus |
| Urbanization, their problems and their remedies | ● Urban Sprawl ● Loss of Agricultural Land ● Rising Aspirations and Migration ● Urban Planning and Role of Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) ● Governance Challenges ● Role in Infrastructure & Service Delivery ● Reforms Required and Government Initiatives Taken So Far ● Smart Cities Mission ● AMRUT ● Swachh Bharat Mission ● Urban Mobility Plans ● Problems of Slums ● Overcrowding ● Health Hazards ● Insecurity of Tenure ● Poor Living Conditions |
| Effects of Globalization on Indian society | Globalisation ● Understanding Globalisation – Its Different Dimensions ● Economic ● Political ● Technological ● Cultural ● Environmental ● Globalisation & Culture ● Cultural Homogenisation ● Glocalisation (Global + Local Cultural Fusion) ● Factors Driving Globalisation ● Advancements in Technology ● Liberalisation of Trade & Economy ● Rise of Multinational Corporations (MNCs) ● Internet and Communication Networks ● Globalisation & India ● Policy Shifts since 1991 ● Integration with Global Markets ● FDI, Outsourcing, IT Boom ● Impact of Globalisation on India ● Socio-Cultural Changes ● Economic Growth & Inequality ● Impact on Women (Employment, Empowerment, Exploitation) ● Effects on Agrarian Sector (Cash Crops, Corporate Farming, Vulnerability) ● Does Globalisation Cause Poverty? ● Debate on Inequality vs. Inclusion ● Mixed Outcomes Based on Region, Class, and Sector ● Role of Policy in Shaping Outcomes |
| Social Empowerment | Globalisation ● Understanding Globalisation – Its Different Dimensions ● Economic ● Political ● Technological ● Cultural ● Environmental ● Globalisation & Culture ● Cultural Homogenisation ● Glocalisation (Global + Local Cultural Fusion) ● Factors Driving Globalisation ● Advancements in Technology ● Liberalisation of Trade & Economy ● Rise of Multinational Corporations (MNCs) ● Internet and Communication Networks ● Globalisation & India ● Policy Shifts since 1991 ● Integration with Global Markets ● FDI, Outsourcing, IT Boom ● Impact of Globalisation on India ● Socio-Cultural Changes ● Economic Growth & Inequality ● Impact on Women (Employment, Empowerment, Exploitation) ● Effects on Agrarian Sector (Cash Crops, Corporate Farming, Vulnerability) ● Does Globalisation Cause Poverty? ● Debate on Inequality vs. Inclusion ● Mixed Outcomes Based on Region, Class, and Sector ● Role of Policy in Shaping Outcomes |
| Communalism | Communalism ● Communalism – Its Characteristics ● Politicization of Religion ● Group Identity over National Identity ● Us vs. Them Mentality ● Intolerance Towards Other Communities ● Communalism in India in the Past ● Colonial Legacy and Divide & Rule ● Partition and Pre-Independence Riots ● Communalism in Contemporary India ● Rise of Identity Politics ● Communal Riots and Hate Crimes ● Media and Social Media Influence ● Causes of Communalism ● Historical Divisions ● Political Mobilisation ● Socio-economic Inequalities ● Lack of Education and Awareness ● Prejudices and Stereotypes ● Consequences of Communalism ● Threat to National Unity ● Communal Violence ● Disruption of Law & Order ● Marginalisation of Minorities ● Measures to Control & Eradicate Communalism ● Promoting Interfaith Dialogue ● Inclusive Education ● Strengthening Law Enforcement ● Responsible Political Conduct ● Media Regulation and Accountability ● Secularism as an Antidote to Communalism ● Equal Respect for All Religions ● Constitutional Safeguards ● Promotion of National Integration |
| Regionalism | Regionalism ● Concept of Region & Regionalism ● Different Forms of Regionalism ● Regionalism in India ● Causes of Regionalism ● Concept of ‘Sons of the Soil’ ● Consequences of Regionalism ● Federalism & Regionalism ● Role of Regional Parties ● Measures to Contain Regionalism ● Regionalism in the International Sphere |
| Secularism | Secularism ● Concept of Secularism ● Indian Model of Secularism ● Secularism in India ● Nature & Practice of Secularism in India ● Uniform Civil Code ● Challenges Faced by Secularism in India ● Measures to Make India Truly Secular |
| World and Indian Geography | |
|---|---|
| Salient features of World’s Physical Geography | Geomorphology ● Origin & Evolution of Earth ● Interior of the Earth ● Distribution of Continents & Oceans ● Plate Tectonic Theory ● Distribution of Earthquakes & Volcanoes ● Rocks & Rock Cycle ● Geomorphic Processes – Endogenic & Exogenic ● Landforms & their Evolution ● Geological Time Scale Oceanography ● Hydrological Cycle ● Seafloor Spreading ● Ocean Floor Configuration ● Temperature & Salinity of Oceans ● Movement of Oceans – Waves, Tides, Currents Climatology ● Earth’s Atmosphere – Composition & Structure ● Solar Radiation, Heat Budget & Temperature ● Atmospheric Circulation & Weather Systems ● World Climate (with examples) Soil Geography ● Soil & Soil Contents ● Process of Soil Formation ● Soil Forming Factors ● Types of Soils (with examples) ● Soil Erosion & Conservation |
| Distribution of Key Natural Resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent) | Resources 🔹 Types of Resources ● On the Basis of Origin – Biotic & Abiotic ● On the Basis of Ownership – Individual, Community, National, International ● On the Basis of Exhaustibility – Renewable & Non-Renewable ● On the Basis of Status of Development – Potential, Developed, Stock, Reserve Land Resources ● Land Utilisation ● Land Use Pattern ● Land Degradation & Conservation Forest Resources ● Types & Distribution – Forests, Grasslands, etc. ● Causes of Depletion ● Conservation of Forests Water Resources ● Marine & Freshwater Resources ● Water Scarcity & Need for Conservation ● Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) Agricultural Resources ● Types of Farming ● Cropping Patterns ● Contribution to Economy, Employment & Output ● Food Security Mineral & Energy Resources 🔹 Mineral Resources ● Classification – Ferrous & Non-Ferrous Minerals ● Occurrence of Minerals ● Conservation of Minerals 🔹 Energy Resources ● Classification – Conventional & Non-Conventional ● Occurrence of Energy Resources ● Conservation of Energy Resources |
| Factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India) | 🔹 Classification of Industries ● Based on Raw Material ● Based on Size ● Based on Ownership ● Based on Nature of Product ● Based on Use 🔹 Location & Distribution of Industries ● Factors Affecting Industrial Location: ● Raw Material ● Labour ● Market ● Capital ● Land ● Grants & Financial Incentives ● Power ● Transport ● Water ● Communication 🔹 Distribution of Major Industries ● Iron & Steel ● Cotton Textile ● Information Technology (IT) 🔹 Types of Industry Clustering ● Agglomeration Industries ● Footloose Industries |
| Important Geophysical Phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features (including Water-bodies and Ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes | 🔹 earthquakes ● Why Does the Earth Shake? ● Earthquake Waves ● Shadow Zone ● Types of Earthquake ● Measuring Earthquake ● Effects of Earthquake 🔹 Tsunamis ● What Causes a Tsunami? ● Effects of Tsunami ● Mitigating the Impact of Tsunami 🔹 Volcanoes ● Types of Volcanoes ● What Causes Volcanoes? ● Volcanic Landforms ● Intrusive Volcanic Landforms ● Extrusive Volcanic Landforms ● Distribution of Volcanoes 🔹 Cyclones ● Tropical Cyclones ● Extra-Tropical Cyclones ● Anti-Cyclone II. Environmental Changes & Impact ● Factors Causing Changes in Critical Geographical Features ● Examples of Changing Geographical Features: ● Melting of Ice Sheets ● Desertification ● Sea-Level Rise ● Deforestation, etc. ● Impact of Changing Geographical Features III. Physical Geography of India ● Physiography of India ● Drainage System ● Climate ● Soils in India ● Natural Vegetation IV. Human Geography ● Demography ● Urbanization ● Census V. Economic Geography ● Agriculture ● Mineral Resources ● Energy Resources ● Industry ● Transport and Communication |
🔗Candidates can get the Previous Year Questions for UPSC Mains GS 4 in the linked article.












