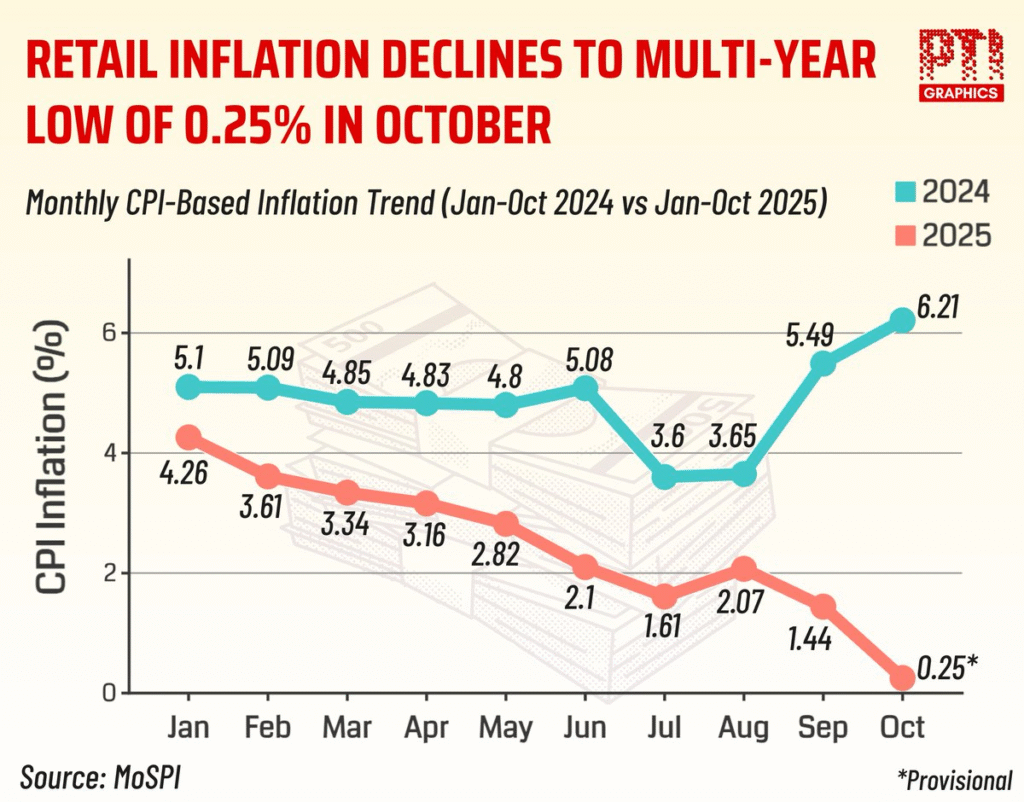
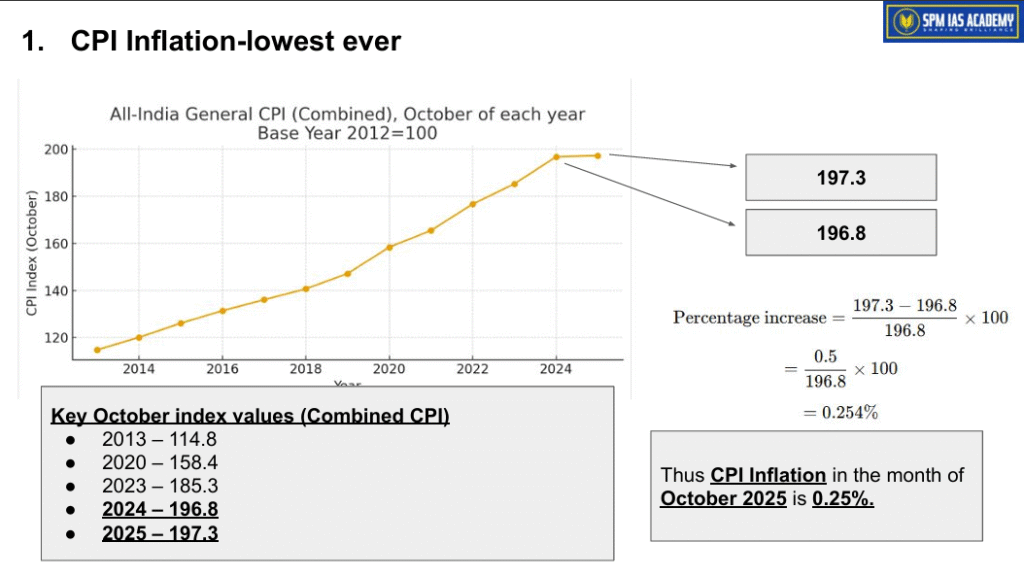
Retail inflation in India has recorded a historic low. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation rate fell to 0.25% in October, 2025. It is the lowest value ever since the current CPI series began in 2012. This development has major implications for the Indian economy, monetary policy, and future interest rates.
This article explains the data, the reasons behind the fall, and the possible response from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It also connects the topic to important areas of UPSC Prelims and Mains.
Why In the News?
- Retail inflation, measured by the CPI, dropped sharply to 0.25% in October, 2025.
- This level is the lowest since the revised CPI series came into effect in 2012.
- The decline surprised many economists because inflation has remained sticky in the past few years.
- However, a combination of factors pushed the inflation number down. Therefore, understanding these factors becomes essential for UPSC aspirants preparing for the Indian Economy.
What is CPI Inflation?
- CPI Inflation refers to the rate at which the general price level of a basket of goods and services increases, leading to a decline in purchasing power.
- The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is the primary measure used to calculate this inflation, based on the price changes in a typical set of consumer goods and services over time.
Components of the CPI Basket:
- The CPI basket consists of a variety of goods and services commonly purchased by households. These include:
- Food and Beverages: Includes items like grains, dairy, and vegetables.
- Housing: Rent, maintenance, and utilities.
- Clothing and Footwear: Apparel and shoes.
- Transportation: Petrol, diesel, and public transport costs.
- Medical Care: Health services, medications, etc.
- Education and Entertainment: School fees, cinema tickets, and recreational activities.
Types of CPI:
- CPI for Industrial Workers (CPI-IW): Used to measure inflation for industrial workers.
- CPI for Urban Non-Manual Employees (CPI-UNME): Reflects inflationary trends affecting salaried employees in urban areas.
- CPI Combined: A combination of CPI-IW and CPI-UNME, giving a broader picture of price changes in the economy.
Calculation of CPI Inflation:

Significance of CPI Inflation:
- Economic Indicator: CPI Inflation is a crucial indicator of the cost of living and purchasing power of the general public.
- Policy Decisions: Helps central banks like the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) decide on monetary policy (interest rates) to control inflation or stimulate the economy.
- Social Welfare: Affects wages, pensions, and benefits. Governments may adjust these according to the CPI to maintain real income levels.
Reasons Behind the Decline in CPI Inflation:
The fall in inflation is not due to a single cause. Several economic factors worked together to reduce price levels. Below are the key reasons.
1. First Full Month Impact of GST Rate Cuts:
- The government recently reduced GST rates on several essential and commonly consumed items. These cuts lowered the final market price of many products. As a result, CPI inflation saw a direct fall during October. This impact became more visible because October was the first full month after the rate cuts.GST-related price changes affect CPI quickly because the index covers a wide basket of goods. Therefore, even small price reductions across categories can bring inflation down.
2. Decline in Food Prices:
- Food items have the highest weightage in the CPI basket. Hence, any change in food inflation strongly affects overall inflation. Food prices dropped by nearly 5% compared to last year.
Vegetables, cereals, and pulses contributed most to the decline. Better supply, reduction in storage costs, and an improved monsoon supported this trend. Since food prices carry almost 45% weight in CPI, the fall in this category had a major impact. Therefore, food inflation became the strongest driver behind the record-low CPI figure.
3. The Base Effect:
- The base effect plays a significant role in inflation measurement.
Inflation in October 2024 was extremely high, especially in food categories.
During that month, food inflation stood at 9.7%. So, this year’s comparison appears lower even if price levels have not fallen drastically. The base effect occurs when the previous year’s index value is unusually high or low. This statistical factor often makes inflation readings appear artificially high or low. Thus, the base effect has amplified the drop in inflation during October.
What Does This Mean for the Indian Economy?
- A sharp fall in inflation reflects lower pressure on household budgets.
- Consumers find essential items cheaper.
- However, extremely low inflation can also indicate weak demand in the economy.
- Therefore, policymakers must respond carefully.
- Low inflation gives the government and the RBI more space for growth-supporting policies.
- Thus, the economic environment becomes more favourable for investment and consumption.
How RBI May Respond to the Record-Low Inflation:
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the RBI manages inflation through various monetary tools.
- The Committee must maintain CPI inflation at 4%, with a tolerance band of 2 – 6%, as per the Monetary Policy Framework Agreement.
- Since inflation has fallen well below this band, the RBI may shift its approach. Following are the possible steps the RBI may take.
- Possible Repo Rate Cut:
- With inflation at a record low, the RBI may consider cutting the repo rate.
- A repo rate cut will make borrowing cheaper for consumers and firms.
- Lower interest rates support credit growth and encourage investment.
- Thus, the RBI may adopt an expansionary monetary policy in its next meeting.
- The repo rate has remained unchanged at 5.5% for two consecutive meetings. But now, with inflation far below the target, the RBI faces pressure to support growth.
- Need for Expansionary Monetary Policy:
- Very low inflation gives the RBI flexibility to ease monetary conditions.
- Expansionary policy supports economic activity during weak periods.
- Therefore, many economists expect the RBI to adopt a more growth-oriented stance.
- If the central bank cuts rates, banks will reduce lending rates. This will boost consumption in sectors like housing, automobiles, and manufacturing.
- Additionally, cheaper loans help businesses expand production.
- Upcoming MPC Meeting:
- The next Monetary Policy Committee meeting is scheduled for December 3–5, 2025.
- The committee will review incoming data on inflation, growth, and global economic conditions. Therefore, the December meeting will be crucial for understanding the RBI’s forward policy direction.
- If inflation continues to remain low, the MPC may take an accommodative approach. However, the RBI may also act cautiously due to global uncertainties.
Satyajit Sir’s Newspaper Analysis: The Best Source of Current Affairs for UPSC and APSC
Retail inflation in India, measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), fell sharply to 0.25% in October 2025, the lowest level since the revised CPI series was introduced in 2012. This unusual drop—especially after years of stubbornly high inflation—was explained in depth by Satyajit Sir during his Newspaper Analysis on 13th November. A combination of easing food prices, improved supply conditions, and stabilising global commodities helped pull inflation down. For aspirants aiming to stay ahead with the best current affairs for UPSC and APSC, Satyajit Sir’s Newspaper Analysis stands out as one of the most reliable and analytical sources, helping students understand not just the news but the economic logic behind it.
Conclusion:
CPI inflation falling to 0.25% marks a historic moment for the Indian economy. The drop reflects GST rate cuts, cheaper food items, and a strong base effect. With inflation far below the targeted range, the RBI may shift toward a more expansionary monetary policy. As India prepares for the next MPC meeting in December, economic watchers expect significant policy signals.
Also read : 8th Pay Commission
Sources:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dhLp1Engazc&t=35s
- https://www.thehindu.com/business/Economy/retail-cpi-inflation-india-october-2025/article70270815.ece
- https://tradingeconomics.com/india/inflation-cpi
The sharp decline in CPI inflation was due to GST rate cuts, a drop in food prices, and the base effect.
The base effect makes inflation appear artificially low or high, as it compares current prices with the previous year’s unusually high or low levels.
The drop indicates lower pressure on household budgets but may also signal weak demand in the economy, requiring careful policymaking.
The RBI may consider cutting the repo rate to stimulate growth, making borrowing cheaper and boosting credit and investment.
Low inflation gives space for expansionary policies, encouraging investment and consumption, but too low inflation could signal sluggish economic growth.












