“Through yoga, language, arts, and spirituality, India turns culture into a quiet force of global influence.”
India holds a unique position in the global arena due to its civilizational depth, cultural diversity, and spiritual heritage. These strengths allow India to practice effective cultural diplomacy and project soft power worldwide. Soft power refers to a country’s ability to influence others through culture, values, and ideas rather than military or economic force. Therefore, understanding India’s soft power strategy is essential for UPSC aspirants.
This blog explains how India uses cultural diplomacy to build global partnerships, strengthen foreign relations, and enhance its global presence.
What Is Soft Power?
- Joseph Nye introduced the concept of soft power. Soft power influences global behaviour through attraction rather than coercion.
- Countries use culture, values, traditions, and diplomacy to gain influence.
- India uses its civilizational heritage to shape global narratives.
- Therefore, soft power remains a key pillar of India’s foreign policy.
Why Cultural Diplomacy Matters for India:
- India’s cultural diplomacy creates goodwill worldwide. It promotes global understanding.
- It strengthens international cooperation and counters misinformation.
- It boosts tourism and the Indian economy and supports India’s global leadership ambitions.
- Therefore, cultural diplomacy plays a vital role in India’s external engagement.
India’s Soft Power Tools:
1. Yoga: India’s Most Recognized Soft Power Tool:
Yoga stands as India’s strongest cultural export. People across the world practice Yoga for health and well-being.

How India Uses Yoga Diplomatically:
- India pushed for International Yoga Day at the UN.
- The UN adopted 21 June as International Yoga Day in 2014.
- Thousands of global Yoga events promote India’s heritage.
- Diplomatic missions organize Yoga camps worldwide.
- Yoga strengthens India’s image as a leader in wellness.
Therefore, Yoga remains a powerful diplomatic instrument.
2. Ayurveda and Indian Traditional Medicine:
Ayurveda and traditional medicine enhance India’s global soft power. Many countries recognize India’s traditional therapies.
Key Initiatives:
- Ministry of AYUSH promotes Ayurveda globally.
- India signs MoUs for Ayurveda centres in foreign nations.
- Indian medical missions promote natural therapy.
- Global demand for herbal products boosts India’s exports.
Therefore, Ayurveda supports India’s health diplomacy and economic outreach.
3. Bollywood and the Global Film Industry:
Bollywood attracts global audiences. Indian films influence fashion, music, and cultural trends. Bollywood connects India with Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America.
How Bollywood Helps Diplomacy:
- Indian movies build cultural familiarity.
- Stars become informal ambassadors of culture.
- Film festivals promote India’s creative industries.
- Co – production agreements expand global reach.
Therefore, Bollywood remains a strong pillar of India’s cultural diplomacy.
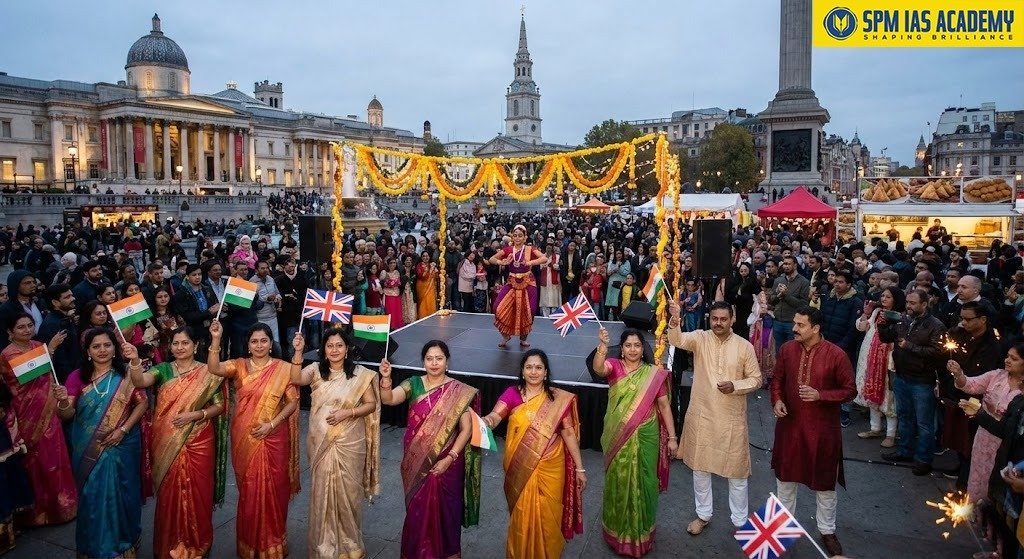
4. India’s Diaspora: A Global Bridge of Culture:
India has one of the world’s largest diasporas. As of May, 2024, there are around 35.42 million overseas Indians living worldwide.

Diaspora Contributions:
- They promote Indian festivals and traditions. The Indian diaspora in the United States organizes New York Diwali at Times Square, one of the largest public celebrations of Indian culture, showcasing classical dance, music, and food.
- They strengthen India’s image in host nations. Sundar Pichai (CEO, Google) and Satya Nadella (CEO, Microsoft) enhance India’s global reputation for innovation, talent, and leadership through their influential roles.
- They support political and economic ties. The Indian – American community played a key role in supporting the India–US Civil Nuclear Agreement (2008) by lobbying American lawmakers and shaping public opinion.
- They influence global business networks. Indian-origin entrepreneurs in Silicon Valley contribute to major investments in Indian startups and tech collaborations, strengthening India’s integration into global supply chains.
- They enhance cultural understanding. Indian diaspora groups in Canada run multicultural workshops, yoga centres, and Hindi schools, helping local communities understand Indian traditions, languages, and values.
India engages with its diaspora through ‘Pravasi Bharatiya Divas’ and ‘Vande Bharat Missions’. Therefore, the diaspora acts as a major soft power resource.
5. Indian Cuisine and Culinary Diplomacy:
Indian food enjoys global popularity. Dishes like biryani, dosa, and samosa appear in global menus.
Diplomatic Impact:
- Food festivals promote cultural connections.
- Indian restaurants create local cultural familiarity.
- Culinary events strengthen diplomatic ties.
- Indian spices boost export markets.
Therefore, cuisine helps India spread cultural goodwill.
For example,
- The “Taste of India” food festival hosted at the United Nations Headquarters in New York showcases Indian regional cuisines and promotes cultural interaction among diplomats.
- India is a major exporter of pepper, cardamom, turmeric, and basmati rice, which are in high demand in Europe, the Middle East, and North America – strengthening India’s trade ties and global culinary influence.
6. Buddhism and India’s Civilizational Legacy:
India is the birthplace of Buddhism. Many Asian countries share deep spiritual links with India.
India’s Buddhist Diplomacy:
- India promotes Nalanda University as a global centre. For example, the revival of Nalanda University in 2014, supported by countries like Japan, China, Thailand, and Singapore, positions India as the intellectual hub of Buddhist studies and cultural exchange.
- India supports Buddhist circuits and heritage sites.
- India hosts Buddhist conclaves with Asian nations.
- India strengthens ties with countries like Japan, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
Therefore, Buddhism anchors India’s diplomacy in Asia.
7. Indian Language Promotion Abroad:
Indian languages gain global recognition. Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, and Telugu have large global communities.
How India Uses Language Diplomacy:
- ICCR promotes Indian languages through cultural centres.
- Universities worldwide teach Indian languages.
- Digital platforms increase global interest in Indian languages.
Therefore, language becomes a powerful cultural connector.
8. Indian Arts, Crafts, and Handloom Traditions:
India’s arts and handloom crafts create global demand. Indian textiles, classical dance, and handicrafts carry deep cultural value.
Cultural Impact:
- India hosts exhibitions and craft melas abroad.
- Dancers and musicians perform through cultural missions.
- Indian artisans participate in global festivals.
- Museums showcase Indian heritage collections.
- For example, the “Festival of India” exhibitions organized in countries like Japan, Russia, and France display Indian textiles, handlooms, and traditional art forms, boosting global appreciation and demand.
Therefore, Indian arts strengthen cultural diplomacy.
9. Festivals as Soft Power Events:
Indian festivals like Diwali, Holi, and Durga Puja are celebrated worldwide. They promote inclusivity and cultural understanding.
Diplomatic Significance:
- Embassies celebrate festivals with global communities.
- Foreign leaders join festival events.
- Festival diplomacy highlights India’s cultural diversity.
Therefore, festivals serve as powerful diplomatic platforms.
10. Digital Diplomacy and Cultural Outreach:
India uses digital tools to promote culture globally.
Digital Soft Power Tools:
- Social media showcases India’s heritage.
- Virtual tours promote cultural sites.
- Digital campaigns spread Yoga and Ayurveda.
- Films and music reach new audiences through OTT platforms.
Therefore, digital diplomacy expands India’s global cultural reach.
11. India’s Role in UNESCO and Cultural Conservation:
India participates actively in UNESCO forums. It promotes global cultural preservation.
Key Contributions:
- India supports world heritage conservation.
- India nominates cultural sites for UNESCO listing.
- India contributes to global cultural diversity.
Therefore, UNESCO platforms enhance India’s cultural visibility.
12. India’s Humanitarian and Educational Diplomacy:
India uses education and humanitarian assistance to build soft power.
Examples:
- India offers scholarships through ICCR.
- India funds schools and cultural centres in friendly nations.
- India sends humanitarian aid during disasters.
- India builds goodwill through development partnerships.
These initiatives deepen India’s international influence.
13. Sports Diplomacy and India’s Global Identity:
Cricket, yoga, and kabaddi create global sports engagement.
Role of Sports:
- Cricket strengthens ties with Commonwealth nations.
- Kabaddi leagues expand to new regions.
- Indian athletes boost national pride.
For example, the Pro Kabaddi League inspired the launch of kabaddi tournaments in countries like Iran, South Korea, Kenya, and Argentina, significantly expanding the sport’s global footprint. India’s dominance in the Kabaddi World Cup further enhances soft power.
Therefore, sports diplomacy adds a dynamic layer to India’s soft power.
14. The International Solar Alliance and Cultural Leadership:
India promotes sustainable development through global alliances.
Impact:
- ISA strengthens India’s climate diplomacy.
- It projects India as a responsible global leader.
- Clean energy cooperation enhances goodwill among the global community.
Therefore, India’s developmental diplomacy complements cultural outreach.
Why Cultural Diplomacy Matters for India’s Foreign Policy:
Cultural diplomacy supports India’s foreign policy in several ways:
- It builds trust with partner nations.
- It strengthens India’s global brand.
- It counters negative narratives about India.
- It promotes national values in global forums.
- It opens doors for trade, tourism, and investment.
- It creates stable long-term partnerships.
Therefore, soft power remains central to India’s foreign policy doctrine.
What are the Challenges to India’s Cultural Diplomacy?
India’s cultural diplomacy faces certain challenges as given below:
- Cultural narratives face competition from global powers.
- Hollywood, K-Pop, and Chinese Confucius Institutes dominate global cultural spaces, making it harder for Indian cinema, literature, and art to gain equivalent visibility.
- Limited funding restricts cultural outreach.
- The Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) operates with a much smaller global outreach budget compared to China’s cultural promotion programs or Japan’s international cultural missions, limiting India’s global cultural presence.
- Misrepresentation of Indian culture in global media continues.
- Western media often portrays India through stereotypical themes—poverty, caste, or exoticism—overlooking India’s diverse cultural, technological, and civilizational strengths, which weakens accurate cultural messaging.
- Diaspora integration issues create periodic tensions.
- Incidents involving Indian communities in countries like Canada or Australia – including hate crimes or community conflicts – sometimes strain local relations and affect India’s diaspora diplomacy.
- Political perceptions affect cultural messaging.
- Global debates on issues like India’s citizenship laws or human rights perceptions occasionally influence how Indian cultural initiatives are received abroad, creating political filters around cultural diplomacy efforts.
Nevertheless, India continues to strengthen its global soft power profile.
Conclusion:
India uses cultural diplomacy to build influence, trust, and goodwill worldwide. Its ancient traditions, modern cultural industries, and global diaspora create a strong soft power foundation. For UPSC aspirants, understanding India’s soft power strategies is essential because these tools shape foreign policy, international relations, and global partnerships.
Sources:
- https://www.bluekraft.in/the-symphony-of-indias-cultural-diplomacy/
- https://www.mea.gov.in/distinguished-lectures-detail.htm?855
- https://iisppr.org.in/projecting-culture-shaping-perceptions-indias-use-of-cultural-diplomacy-in-global-engagement/
- https://prsindia.org/policy/report-summaries/india-s-soft-power-and-cultural-diplomacy
The Cultural Diplomacy of India refers to the use of yoga, Ayurveda, festivals, arts, cinema, and civilizational heritage to build goodwill, influence global opinion, and strengthen international partnerships through soft power.
Yoga enhances India’s global image as a leader in wellness. With International Yoga Day celebrated in over 190 countries, yoga events organized by Indian embassies help promote India’s values, spirituality, and cultural influence worldwide.
India’s 35+ million–strong diaspora promotes festivals, cuisine, languages, and cultural traditions abroad. They act as cultural bridges and support India’s political, economic, and diplomatic ties with host countries.
Bollywood films and music have large audiences in Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America. Indian movies shape global cultural familiarity, influence fashion and trends, and act as powerful non-official ambassadors of Indian society and creativity.
Cultural diplomacy helps India build trust, counter misinformation, attract tourism, open trade opportunities, strengthen development partnerships, and project itself as a responsible global leader—especially in multilateral forums like the UN and UNESCO.












