India’s space journey reflects ambition, discipline, and innovation. Over the decades, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has launched missions that reshaped India’s space capabilities and strengthened its global standing.
For UPSC aspirants, these missions are crucial for Prelims, GS-3, Essays, and Interview.
Therefore, this article explains the Top 10 ISRO missions that transformed India’s space exploration path.
Top 10 ISRO Missions That Changed the Face of Space Exploration:
Aryabhata (1975) – India Enters the Space Age
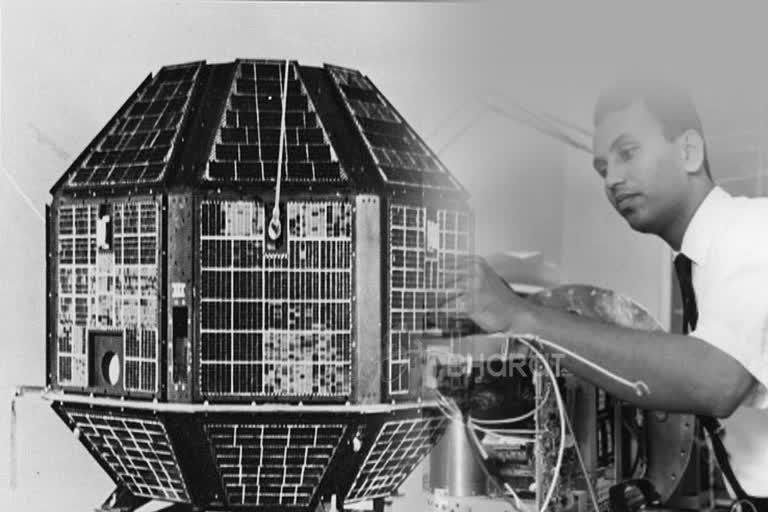

- ISRO launched Aryabhata, India’s first satellite, in 1975.
- It marked India’s official entry into space technology.
- Moreover, it gave scientists the confidence to design and build future satellites independently.
- Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket launched Aryabhata.
SLV-3 (1980) – India Builds Its First Launch Vehicle

- ISRO developed and launched the SLV-3, India’s first indigenous rocket, in 1980.
- It was India’s first experimental launch vehicle which was an all solid, four stage vehicle.
- It successfully placed the Rohini satellite in orbit on 18 July, 1980. Consequently, India gained the capability to launch satellites on its own.
- It showed the way to the advanced launch vehicle projects – ASLV, PSLV, GSLV.
INSAT Series (1983 – Present) – India Strengthens Communication

- ISRO deployed the Indian National Satellite (INSAT) system is one of the largest domestic communication satellite systems in Asia- Pacific region.
- It has nine operational communication satellites placed in Geo-stationary orbit.
- This series aimed to transform communication, broadcasting, and weather forecasting.
- With the commissioning of INSAT-1B, it initiated a major revolution in India’s communication sector.
- These satellites enhanced India’s disaster warning systems and boosted digital connectivity across the country.
IRS Series (1988–Present) – India Leads in Remote Sensing

- ISRO launched the IRS series to build one of the world’s largest remote-sensing satellite systems.
- These satellites support agriculture, water management, forestry, and urban planning.
- As a result, India gained global leadership in earth observation.
Chandrayaan-1 (2008) – India Discovers Water on the Moon

- ISRO sent Chandrayaan-1 to the Moon on October 22, 2008 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
- The spacecraft carried 11 scientific instruments built in India, USA, UK, Germany, Sweden and Bulgaria.
- Its instruments detected water molecules on the lunar surface, a finding that changed global lunar science.
- Moreover, it established India as a serious space research nation.
- The mission came to a conclusion when the communication with the spacecraft was lost on 29th August, 2009.
Mangalyaan – Mars Orbiter Mission (2013)

- Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), India’s first interplanetary mission to planet Mars was launched on board PSLV-C25 on November 05, 2013.
- ISRO achieved history by sending Mangalyaan to Mars in its very first attempt.
- India became the first Asian nation to reach Mars and the only country to succeed on the first try.
- Mangalyaan’s primary objective was to progress the technologies required for interplanetary missions.
- It carried five scientific instruments to study the Martian surface, morphology, atmosphere, and mineralogy from orbit.
- Additionally, it completed the mission with the world’s lowest budget for a Mars mission.
AstroSat (2015) – India Builds a Space Observatory
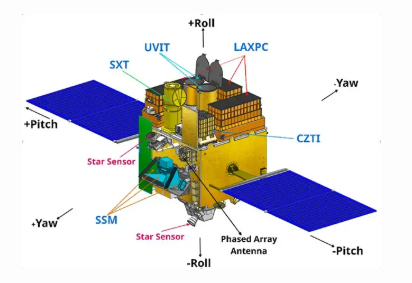
- ISRO launched AstroSat, India’s first multi-wavelength space observatory, in 2015.
- PSLV-C30 rocket was used to carry AstroSat to its orbit.
- AstroSat carried a total of five scientific payloads. They enabled imaging, studying temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra- galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- The unique feature of this observatory is its capability for carrying out broad band simultaneous multi-wavelength observation. It goes from far ultra violet to gamma rays.
- It studies black holes, neutron stars, and cosmic radiation.
- Consequently, India joined an elite group of nations with space telescopes.
GSAT-11 (2018) – India Expands Satellite Internet

- ISRO on 5th December, 2018, launched GSAT-11, its heaviest communication satellite, to improve broadband capacity.
- It was launched from Kourou launch base, French Guiana by Ariane-5 VA-246.
- GSAT-11 was launched into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit. It will play a vital role in providing broadband services across the country reducing digital inequality.
- It will also provide a platform to demonstrate new generation applications.
- It supports Digital India and enhances internet connectivity in remote and rural regions.
Chandrayaan-2 (2019) – India Pushes Advanced Lunar Exploration

- ISRO launched Chandrayaan-2 to study the Moon’s south polar region.
- It comprised an Orbiter, Lander and Rover to explore the unexplored South Pole of the Moon.
- The mission aimed to expand lunar scientific knowledge through comprehensive studies of:
- Topography of the Moon’s surface
- Seismography to understand lunar quakes
- Mineral identification and distribution across the lunar terrain
- Surface chemical composition
- Thermo-physical properties of the lunar topsoil
- Composition of the thin lunar atmosphere
- Although the lander did not achieve a soft landing, the orbiter continues to deliver high-resolution lunar data.
- Moreover, it provided critical experience for Chandrayaan-3.
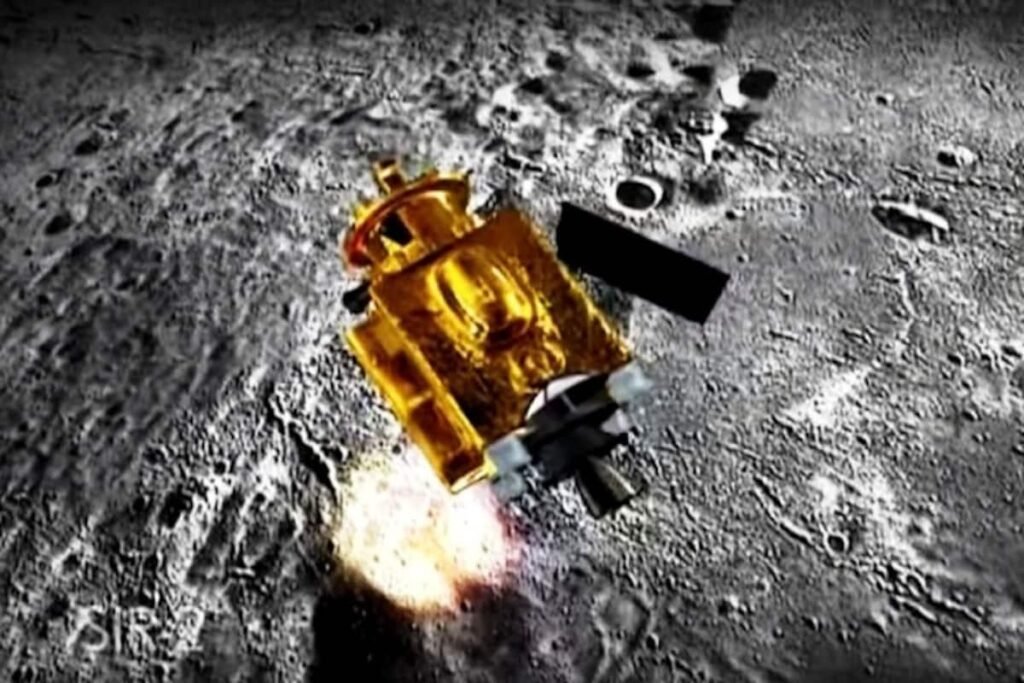
Chandrayaan – 3 (2023) – India Lands Near the Lunar South Pole
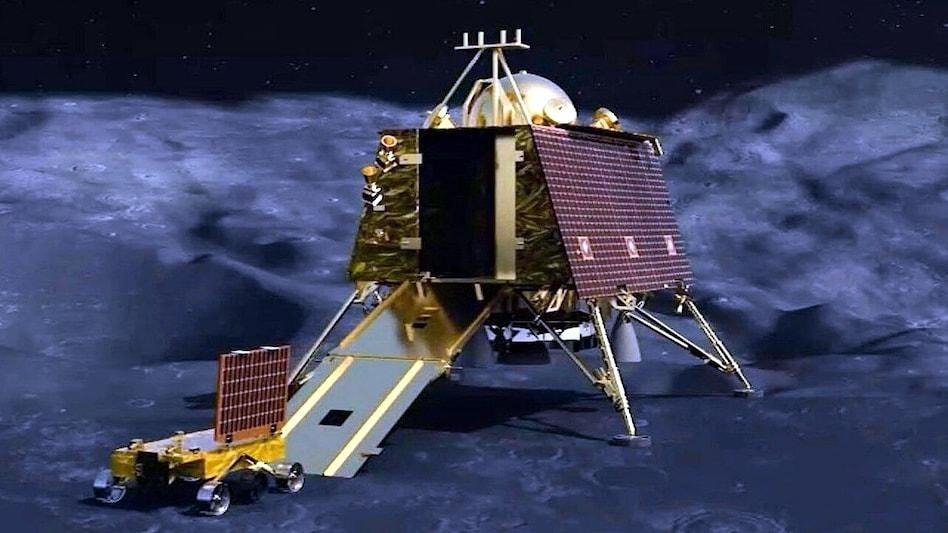

- ISRO created history by landing the Vikram lander near the Moon’s south pole.
- It was launched by LVM3 from SDSC SHAR, Sriharikota.
- The mission objectives of Chandrayaan-3 are:
- To demonstrate Safe and Soft Landing on Lunar Surface
- To demonstrate Rover roving on the moon and
- To conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
- It consists of Lander and Rover configuration.
- Its Rover explored the surface and conducted mineral analysis.
- Consequently, India became the first country to achieve this milestone.
Other Important Missions:
- Gaganyaan Mission – India’s first human spaceflight programme.
- Aditya-L1 – India’s solar observatory at Lagrange Point 1.
- PSLV – World’s most reliable satellite launch vehicle.
- GSLV Mk-III (LVM3) – Heavy-lift rocket for deep-space missions.
Why These ISRO Missions Matter for UPSC Aspirants:
- These missions hold high importance for UPSC science and tech preparation, as they frequently appear in UPSC Prelims and GS-3 Science and Technology.
- Understanding India’s major space milestones helps aspirants write stronger answers in GS-3, enrich their Essay content, and present informed viewpoints during the UPSC Interview.
- Moreover, these missions highlight India’s space achievements UPSC expects candidates to know, and they offer valuable insights into India’s technological progress and global leadership in space exploration.
Conclusion:
ISRO’s achievements reflect India’s growing confidence in science and technology. These Top 10 ISRO missions demonstrate how India moved from launching its first satellite in 1975 to achieving a historic lunar south pole landing in 2023.
Therefore, mastering these missions helps UPSC, APSC and other State Public Service Commission Exam aspirants elevate their answers and stay updated with India’s space advancements.
Sources:
- https://www.isro.gov.in/National_space_day_2024_celebrations.html
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/science/isro-successful-missions-that-made-history/articleshow/111843329.cms
- https://www.isro.gov.in/Chandrayaan3_Details.html
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/science/list-of-isros-space-missions-from-aryabhata-to-chandrayaan/articleshow/112741477.cms
Key ISRO missions include Aryabhata, SLV-3, INSAT, IRS, Chandrayaan-1, Mangalyaan, AstroSat, GSAT-11, Chandrayaan-2, and Chandrayaan-3.
Chandrayaan-3 is significant because it achieved a successful soft landing near the Moon’s south pole, making India the first country to land in this region.
Mangalyaan gained global recognition for reaching Mars orbit on the first attempt and for being one of the world’s most cost-effective interplanetary missions.
The INSAT series revolutionized communication by supporting telecommunication, broadcasting, meteorology, and disaster warning services across the country.
AstroSat serves as India’s first space observatory, designed to study celestial bodies across multiple wavelengths—from ultraviolet to X-rays and gamma rays.












