It’s 2026, and be it academic or any other reason, it’s important to know about the Indian States and Capitals 2025. And most importantly, if you are an UPSC aspirant and preparing for the state civil service preparation, you must have a crystal clear knowledge of each region, the capital city, the primary language, and the cultural significance it holds.
Check now: UPSC Notification 2026 out
Why the Indian State and Capital 2026 Must Be Memorized
In this article, we will discuss the list and the importance of memorizing the Indian States and Capitals 2026. We often see the MCQs regarding the Indian States and the Capital in various government job exams. Most importantly, it is the foundation of geographical literacy. Moreover, if you participate in national-level quizzes and interviews, you should have such basic knowledge.
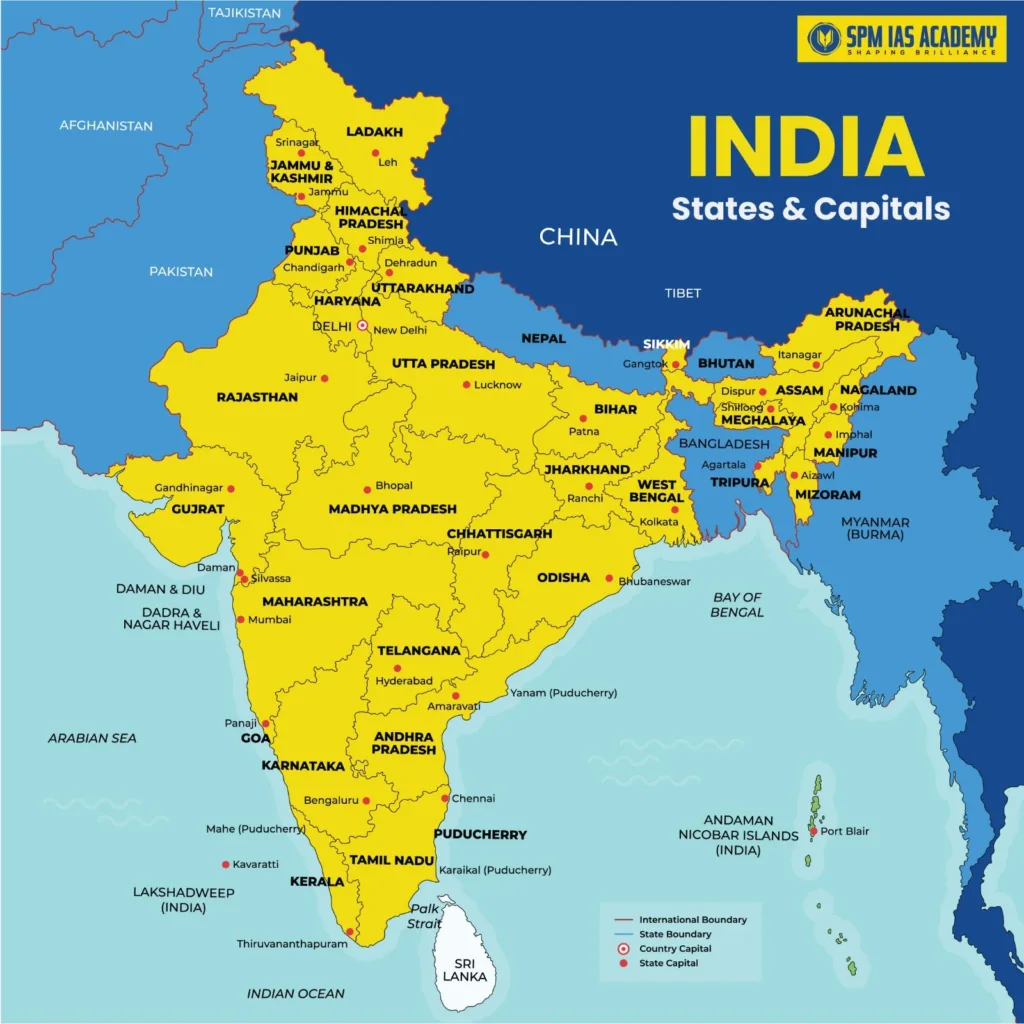
Indian States and Their Capitals 2026(Updated Table)
Every state has its corresponding capital city. Here is the complete list of all 28 states in India, their capitals, and their respective formation dates:
| Sl.No. | Name of theState | Capital | Date of Formation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Amaravati | 1 November 1956 |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar | 20 February 1987 |
| 3 | Assam | Dispur | 1950 |
| 4 | Bihar | Patna | 1950 |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Raipur | 1 November 2000 |
| 6 | Goa | Panaji | 30 May 1987 |
| 7 | Gujarat | Gandhinagar | 1 May 1960 |
| 8 | Haryana | Chandigarh | 1 November 1966 |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | Shimla | 25 January 1971 |
| 10 | Jharkhand | Ranchi | 15 November 2000 |
| 11 | Karnataka | Bengaluru | 1 November 1956 |
| 12 | Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram | 1 November 1956 |
| 13 | Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal | 1 November 1956 |
| 14 | Maharashtra | Mumbai | 1 May 1960 |
| 15 | Manipur | Imphal | 21 January 1972 |
| 16 | Meghalaya | Shillong | 21 January 1972 |
| 17 | Mizoram | Aizawl | 20 February 1987 |
| 18 | Nagaland | Kohima | 1 December 1963 |
| 19 | Odisha | Bhubaneswar | 1950 |
| 20 | Punjab | Chandigarh | 1 November 1966 |
| 21 | Rajasthan | Jaipur | 30 March 1949 |
| 22 | Sikkim | Gangtok | 16 May 1975 |
| 23 | Tamil Nadu | Chennai | 1 November 1956 |
| 24 | Telangana | Hyderabad | 2 June 2014 |
| 25 | Tripura | Agartala | 21 January 1972 |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow | 24 January 1950 |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | Dehradun | 9 November 2000 |
| 28 | West Bengal | Kolkata | 1950 |
Also read : India’s River System 💧
Union Territories and Their Capitals 2026
Let’s learn about the Union Territories. Each Union Territory shares a capital or serves multiple administrative roles.
| Name of the Union Territory | Capital |
|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu | Daman |
| Delhi | New Delhi |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (Summer) / Jammu (Winter) |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti |
| Puducherry | Pondicherry |
| Ladakh | Leh |
Recent Developments & Evolving Borders and Capitals
- While learning about Indian States and Capitals 2026, you can see a landmark change in 2019. Parliament passed the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act and set October 31st as the formation date for the Union Territories of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh.
- Historians consider this event as unprecedented in the history of Indian States and Capitals, because no state had ever been converted into two Union Territories before.
- The total number of Union Territories was officially updated to eight from January 26th, 2020, following the enactment of the Reorganisation Act.
- Daman and Diu were merged with Dadra and Nagar Haveli to create a single Union Territory on January 26th, 2020, as legislated by Parliament.
- States like Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttarakhand conduct legislative sessions in different capital cities, depending on the season, summer and winter capitals.
- The Union Territory of Ladakh has two administrative capitals – Leh and Kargil, to ensure balanced governance and outreach in the mountainous region.
Key Highlights for Indian State and Capital 2026
To ensure better retention, go through the following highlights about the Indian State and Capital below :
- The capital of Telangana is Hyderabad. It also shares a border with Andhra Pradesh temporarily.
- Chandigarh serves as the capital of both Haryana and Punjab.
- Jammu and Kashmir has dual capitals: Srinagar in summer and Jammu in winter.
- Among all capitals, New Delhi holds the most political significance as the National Capital.
Special Features of Indian States and Capitals
Each region has its own distinct cultural, geographical, or historical value. Several states celebrate it’s unique attributes that set them apart.
| State | Special Feature (As per Indian State and Capital 2025) |
|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Andhra Pradesh has been noted for its spicy cuisine and iconic landmarks. Notably, Charminar has been highlighted, although it is currently located in Telangana, its association with Andhra’s cultural history has been acknowledged in the Indian State and Capital 2026 |
| Assam | Assam has been featured for its lush tea gardens and the world-famous Kaziranga National Park. Furthermore, its ecological diversity has been officially emphasized in the Indian State and Capital 2026 list. |
| Bihar | Bihar’s heritage has been showcased with sites like Bodh Gaya and ancient Pataliputra. As a result, it has been classified as historically rich in the Indian State and Capital 2026 database. |
| Goa | Goa’s scenic beaches and lively nightlife have been well documented. Moreover, its cultural influence from Portuguese colonization has also been noted in the Indian State and Capital 2026. |
| Kerala | Kerala has been acclaimed for its serene backwaters and Ayurveda. Consequently, its role as a wellness destination has been strongly featured in the Indian State and Capital 2026. |
| Maharashtra | Maharashtra’s importance has been cemented by its economic stature and cultural exports like Bollywood. Hence, it has been prominently included in the Indian State and Capital 2026 as a leading state. |
| Himachal Pradesh | Himachal Pradesh has been recognized for its breathtaking hill stations and adventure activities. Likewise, tourism’s role in the state’s identity has been emphasized in the Indian State and Capital 2026. |
| Tamil Nadu | Tamil Nadu has been acknowledged for its classical Bharatanatyam dance and temple architecture. Therefore, the state’s traditional arts have been given notable placement in the Indian State and Capital 2026. |
Also read: India’s River System 💧
Difference Between States and Union Territories in the Indian States and Capitals
While learning about the Indian State and Capital, you can see a clear distinction between states and union territories. To clarify, there are state governments in states, while the Central government directly administers the Union Territories. Only a few Union Territories have received legislative assemblies under special provisions.
| Aspect | States | Union Territories |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative Head | Governor | Administrator or Lieutenant Governor |
| Government Type | Elected by the people | Managed by the central government |
| Powers | Federal relationship with the Centre | Unitary relationship with the Centre |
Therefore, you can see a structural difference in the Indian State and Capital 2025 to distinguish governance models across regions.
Number of States in India and Their Capitals in 2026
According to the Indian State and Capital 2025 record, there are 28 states and 8 union territories. Each of these has a specific capital that holds administrative as well as cultural significance.
Indian States, Their Capitals, and Languages
While talking about the Indian State and Capital 2026, also know about the primary language of each state. In addition, you need to understand these connections to encourage and strengthen regional awareness.
| State | Capital | Language(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Amaravati | Telugu |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar | English |
| Assam | Dispur | Assamese |
| Bihar | Patna | Hindi |
| Chhattisgarh | Raipur | Hindi |
| Goa | Panaji | Konkani |
| Gujarat | Gandhinagar | Gujarati |
| Haryana | Chandigarh | Hindi |
| Himachal Pradesh | Shimla | Hindi |
| Jharkhand | Ranchi | Hindi |
| Karnataka | Bengaluru | Kannada |
| Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram | Malayalam |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal | Hindi |
| Maharashtra | Mumbai | Marathi |
| Manipur | Imphal | Meitei (Manipuri) |
| Meghalaya | Shillong | English |
| Mizoram | Aizawl | Mizo |
| Nagaland | Kohima | English |
| Odisha | Bhubaneswar | Odia |
| Punjab | Chandigarh | Punjabi |
| Rajasthan | Jaipur | Hindi |
| Sikkim | Gangtok | English, Nepali |
| Tamil Nadu | Chennai | Tamil |
| Telangana | Hyderabad | Telugu |
| Tripura | Agartala | Bengali, Kokborok |
| Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow | Hindi |
| Uttarakhand | Dehradun | Hindi |
| West Bengal | Kolkata | Bengali |
Union Territories and Languages
The central government has direct control over the Union Territories. Though some have been provided with partial state-like administrative autonomy. Furthermore, you can find that each Union Territory has an official language, which reflects its historical and cultural setting.
Go through the following information regarding Union Territories, their capitals, and their official languages, based on the latest update in Indian States and Capitals 2025:
| Union Territories | Capital | Date of Formation | Official Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair | 1st Nov 1956 | Hindi, English |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh | 1st Nov 1966 | English |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu | Daman | 26th Jan 2020 | Gujarati, Konkani, Marathi, Hindi |
| Delhi | New Delhi | 9th May 1905 | Hindi, English |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (Summer)Jammu (Winter) | 31st Oct 2019 | Kashmiri, Dogri, Hindi, Urdu, English |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti | 1st Nov 1956 | Malayalam |
| Puducherry | Pondicherry | 1st Nov 1954 | Tamil, French, English |
| Ladakh | Leh | 31st Oct 2019 | Hindi, English |
Why New Capitals Are Being Established in Indian States and the Capitals
At present, the concept of shifting or building new capitals has gained traction in the context of the Indian State and Capital. Often, population growth, regional imbalance, and urban congestion have necessitated these moves. For instance, Raipur was replaced by Naya Raipur to accommodate future governance needs.
Moreover, the proposed development of Amaravati was undertaken to create an administrative capital that aligns with Andhra Pradesh’s future vision. Consequently, emphasis has been placed on decentralization and technology-enabled governance. In this way, the evolving nature of the Indian State and Capital reflects India’s adaptive federal system.
Impact of Linguistic and Ethnic Diversity on the Indian State and Capital
Historically, one of the primary reasons for state reorganization has been linguistic and ethnic diversity. Due to this, Parliament passed the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 to form states on linguistic lines. Since then, many changes have continued to occur in the Indian State and Capital due to sociocultural pressures.
For example, Parliament created Nagaland in 1963 to recognize the distinct identity of the Naga people. Later, Mizoram and Meghalaya also got statehood in response to similar demands. Therefore, language and culture continue to play a vital role in defining the Indian State and Capital 2025.
Upcoming Proposals Affecting the Indian State and Capital
In recent years, proposals for new states such as Vidarbha (from Maharashtra), Gorkhaland (from West Bengal), and Harit Pradesh (from Western UP) have gained momentum. Although the government has not officially created these states, their implications for the Indian States and Capitals remain significant.
Eventually, if these demands get approval, the total number of Indian states and union territories may rise again. Thus, the composition of the Indian State and Capital is likely to remain dynamic for years to come.
Important Facts About Indian States and Capitals
- The government merged Daman and Diu with Dadra and Nagar Haveli on January 26th, after Parliament approved a bill during its winter session.
- Due to this merger, officials have revised the total number of Union Territories listed under Indian States and Capitals 2025 to eight.
- Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Uttarakhand have different capitals for summer and winter legislative functions.
- Ladakh also has two capitals- Leh and Kargil – to handle governance and development effectively.
- India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 Union Territories, resulting in a total of 36 distinct administrative entities
- The states and Union Territories are subdivided into districts and local governance units for improved administration.
- Moreover, a Chief Minister leads each state. He/she is responsible for managing the executive branch.
- Regarding Indian States and Capitals, always remember that the judicial, administrative, and legislative powers are usually concentrated in the same capital city, although some states have distributed these functions across different locations.
- Till now, India consists of more than 4,000 towns and cities, showcasing its vast and diverse urban structure.
- Notably, the eight metropolitan cities listed under Indian States and Capitals 2025 include Kolkata, Mumbai, New Delhi, Chennai, Hyderabad, Bangalore, Ahmedabad, and Pune.
- Lastly, Indore city has received the award of the Smart City title for four consecutive years, making it a role model in urban governance.
States & Capitals of India 2025 – Top 5 States in Population
States and Capitals of India 2025 – Top 5 States in Sex Ratio
- Kerala: 1084 women per 1000 men (Highest in India)
- Puducherry: 1038 women per 1000 men
- Tamil Nadu: 995 women per 1000 men
- Andhra Pradesh: 992 women per 1000 men
- Chhattisgarh: 991 women per 1000 men
- Manipur: 987 women per 1000 men (Closely following)
States and Capitals of India 2025 – Top 5 States in Literacy Rate
- Kerala: 94% literacy (Highest in India)
- Mizoram: 91% literacy
- Delhi: 89% literacy
- Goa: 88% literacy
- Himachal Pradesh: 87% literacy
States and Capitals of India 2025 – Top 5 States in Area
- Rajasthan: 342,239 sq. km (Largest state by area)
- Madhya Pradesh: 308,252 sq. km
- Maharashtra: 307,713 sq. km
- Uttar Pradesh: 240,928 sq. km
- Gujarat: 196,024 sq. km
Tips for Memorizing Indian States and Capitals
Even though the list appears long, certain strategies can be adopted to memorize the Indian States and Capitals effectively:
- Flashcards can be used to test yourself daily.
- Mnemonic devices should be created for tricky names.
- Maps should be labelled and revised frequently.
- Grouping by region (North, South, East, West, Northeast) can aid retention.
Also read : India’s River System 💧
Conclusion
To conclude, you need to adopt a strategic and systematic approach to memorize the Indian State and Capital. Since this knowledge plays a critical role in school curricula, civil service exams, and public discourse, it should not be ignored. With updated data, regular revision, and visual aids, you can have complete command over Indian geography.
Citations
- States and Union Territories
- Indian States
- Different Dance Forms Of India With States
- List of India’s 8 union territories and their capitals
- States with the Highest Sex Ratio
- Population
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Indian State and Capital 2025
There are 28 states listed across the country.
There are 8 union territories in India
Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra.
Telangana is the newest state in India, formed in 2014.
As of 2025, India has 28 states and 8 Union Territories. Jammu and Kashmir was reorganized into two Union Territories in 2019, reducing the total number of states from 29 to 28.
Yes, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu were merged into one union territory in 2020, as reflected in Indian States and Capitals 2025.















